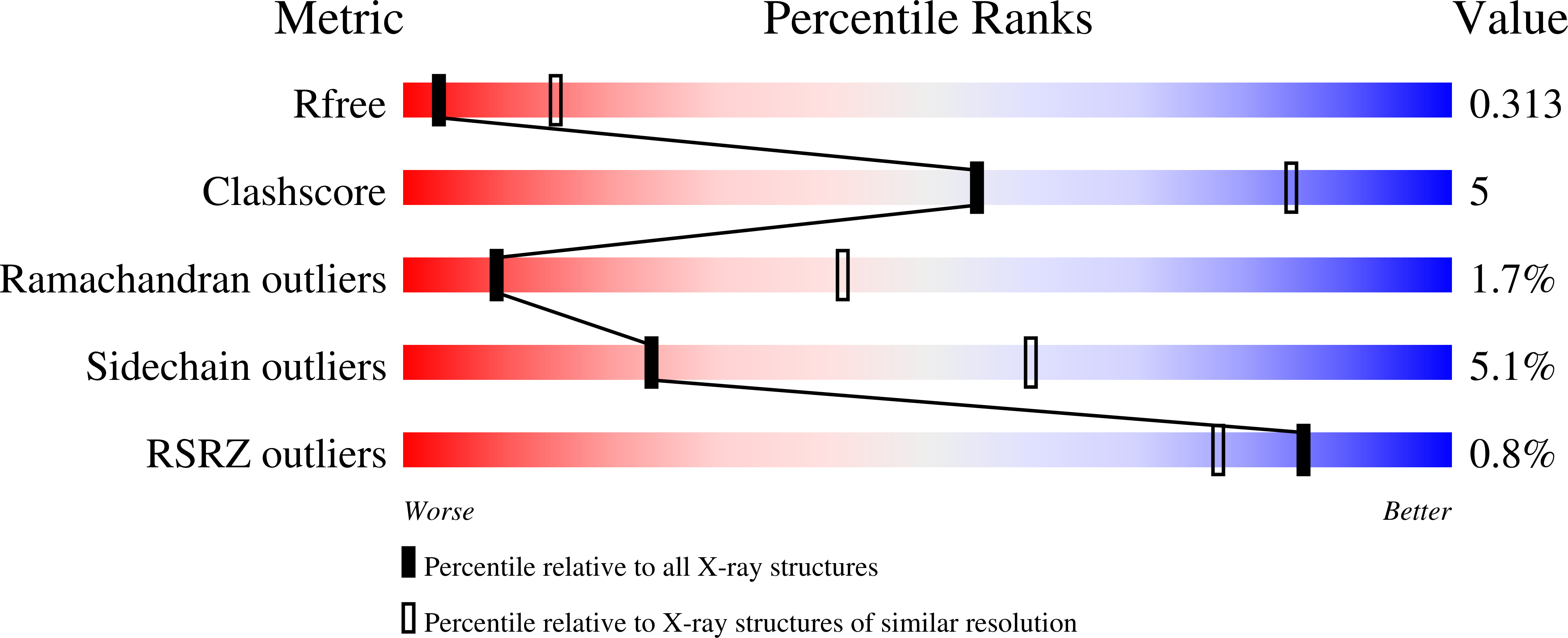
Flexibility of EF-hand motifs: Structural and thermodynamic studies of Calcium Binding Protein- 1 from Entamoeba histolytica with Pb2+, Ba2+, and Sr2+
Kumar, S., Ahmed, E., Kumar, S., Khan, R.H., Gourinath, S.(2012) BMC Biophys 5: 15-15
- PubMed: 22906057
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-1682-5-15
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3ULG - PubMed Abstract:
EF-hand proteins can be activated by the binding of various heavy metals other than calcium, and such complexes can disturb the calcium-signaling pathway and cause toxicity and disease causing state. So far, no comprehensive study has been done to understand different heavy metals binding to calcium signaling proteins. In this work, the flexibility of the EF-hand motifs are examined by crystallographic and thermodynamic studies of binding of Pb2+, Ba2+ and Sr2+ to Calcium Binding Protein-1 from Entamoeba histolytica (EhCaBP1). The structures of the EhCaBP1- heavy metal complexes are found to be overall similar, nevertheless specific differences in metal coordination, and small differences in the coordination distances between the metal and the ligands in the metal binding loop. The largest such distances occur for the Ba2+- EhCaBP1 complex, where two bariums are bound with partial occupancy at the EF2 motif. Thermodynamic studies confirm that EhCaBP1 has five binding sites for Ba2+ compared to four binding sites for the other metals. These structures and thermodynamic studies reveal that the EF-hand motifs can accommodate several heavy atoms with similar binding affinities. The binding of Ca2+ to the 1st, 2nd and 4th sites and the binding of Ba2+ to the 1st, 2nd, 4th and 5th sites are both enthalpically and entropically driven, whereas the binding of Sr2+ to the 1st, 2nd and 4th sites are simply enthalpy driven, interestingly in agreement with ITC data, Sr2+ do not coordinate with water in this structure. For all the metals, binding to the 3rd site is only entropy driven. Energetically, Ca2+ is preferred in three sites, while in one site Ba2+ has better binding energy. The Sr2+-coordination in the EF hand motifs is similar to that of the native Ca2+ bound structure, except for the lack of water coordination. Sr2+ coordination seems to be a pre-formed in nature since all seven coordinating atoms are from the protein itself, which also correlates with entropy contributions in Sr2+ binding. These findings improve our understanding of metal association with calcium binding proteins and of metal induced conformational changes.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Life Sciences, Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi, India. samudralag@yahoo.com.