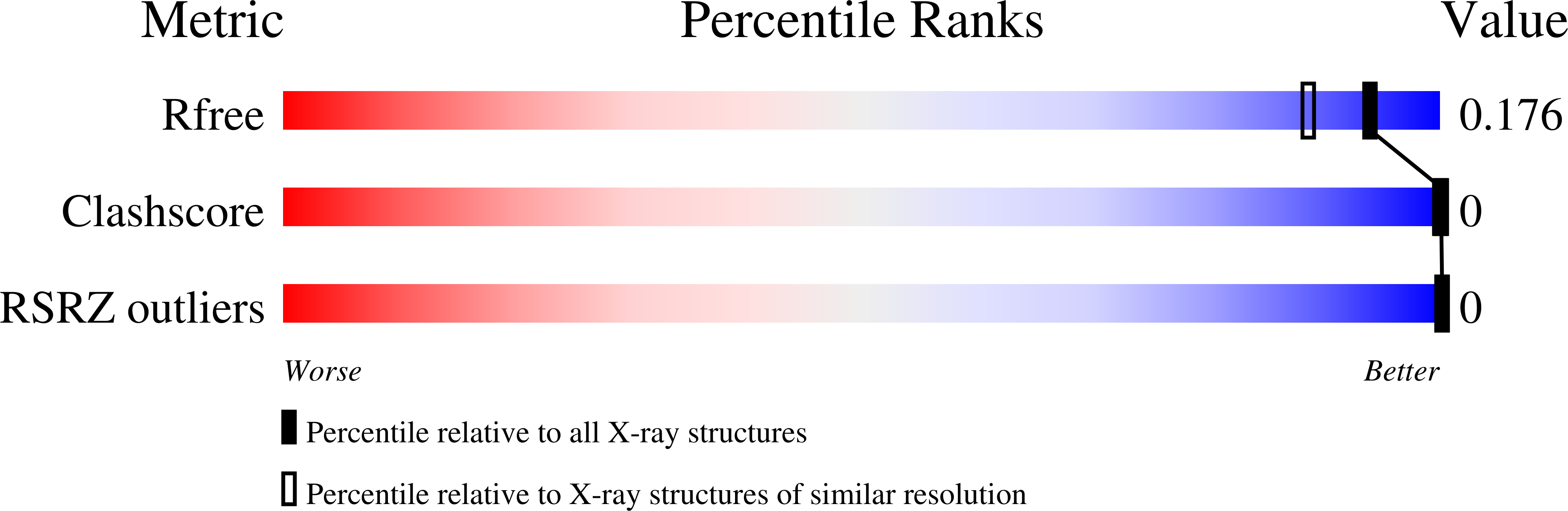Reintroducing electrostatics into macromolecular crystallographic refinement: application to neutron crystallography and DNA hydration.
Fenn, T.D., Schnieders, M.J., Mustyakimov, M., Wu, C., Langan, P., Pande, V.S., Brunger, A.T.(2011) Structure 19: 523-533
- PubMed: 21481775
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2011.01.015
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3QBA - PubMed Abstract:
Most current crystallographic structure refinements augment the diffraction data with a priori information consisting of bond, angle, dihedral, planarity restraints, and atomic repulsion based on the Pauli exclusion principle. Yet, electrostatics and van der Waals attraction are physical forces that provide additional a priori information. Here, we assess the inclusion of electrostatics for the force field used for all-atom (including hydrogen) joint neutron/X-ray refinement. Two DNA and a protein crystal structure were refined against joint neutron/X-ray diffraction data sets using force fields without electrostatics or with electrostatics. Hydrogen-bond orientation/geometry favors the inclusion of electrostatics. Refinement of Z-DNA with electrostatics leads to a hypothesis for the entropic stabilization of Z-DNA that may partly explain the thermodynamics of converting the B form of DNA to its Z form. Thus, inclusion of electrostatics assists joint neutron/X-ray refinements, especially for placing and orienting hydrogen atoms.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular and Cellular Physiology and Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA.