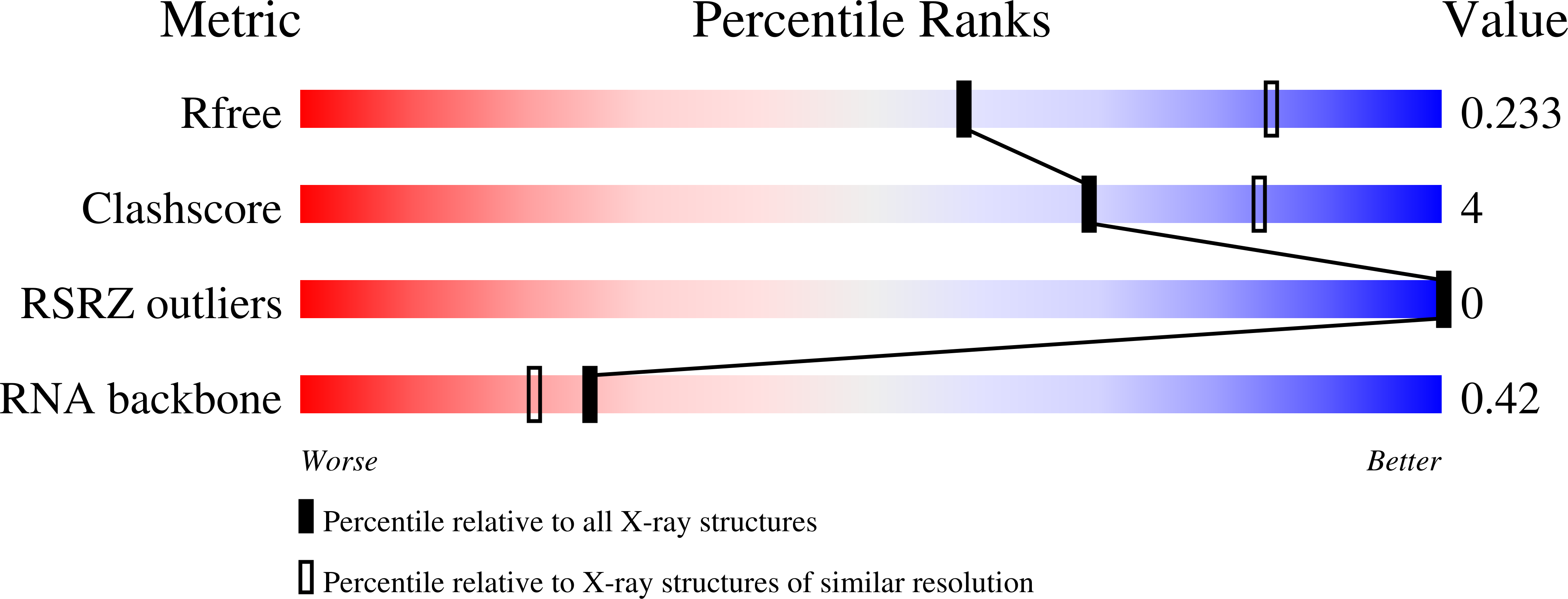The Crystal Structure of the CeNA:RNA Hybrid ce(GCGTAGCG):r(CGCUACGC).
Ovaere, M., Herdewijn, P., Van Meervelt, L.(2011) Chemistry 17: 7823-7830
- PubMed: 21618623
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201003594
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3KNC - PubMed Abstract:
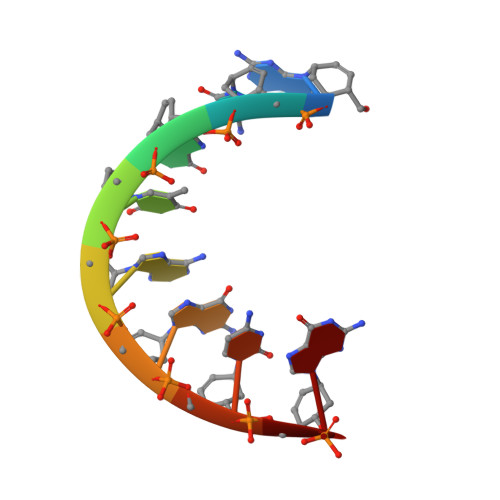
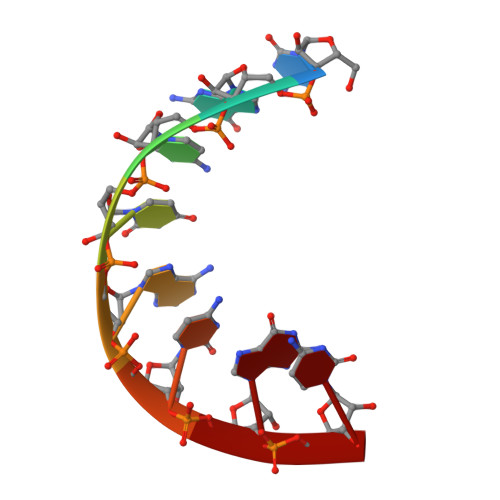
Cyclohexenyl nucleic acids (CeNA) are characterised by the carbon-carbon double bond replacing the O4'-oxygen atom of the natural D-2'-deoxyribose sugar ring in DNA. CeNAs exhibit a high conformational flexibility, are stable against nuclease activity and their hybridisation is RNA selective. Additionally, CeNA has been shown to induce an enhanced biological activity when incorporated in siRNA. This makes CeNA a good candidate for siRNA and synthetic aptamer applications. The crystal structure of the synthetic CeNA:RNA hybrid ce(GCGTAGCG):r(CGCUACGC) has been solved with a resolution of 2.50 Å. The CeNA:RNA duplex adopts an anti-parallel, right-handed double helix with standard Watson-Crick base pairing. Analyses of the helical parameters revealed the octamer to form an A-like double helix. The cyclohexenyl rings mainly adopt the (3)H(2) conformation, which resembles the C3'-endo conformation of RNA ribose ring. This C3'-endo ring puckering was found in most of the RNA residues and is typical for A-family helices. The crystal structure is stabilised by the presence of hexahydrated magnesium ions. The fact that the CeNA:RNA hybrid adopts an A-type double helical conformation confirms the high potential of CeNAs for the construction of efficient siRNAs which can be used for therapeutical applications.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Celestijnenlaan 200F-box 2404, 3001 Leuven, Belgium.