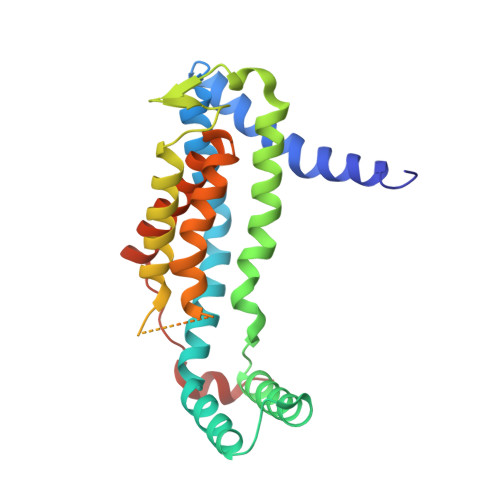
Structural basis of Sec-independent membrane protein insertion by YidC.
Kumazaki, K., Chiba, S., Takemoto, M., Furukawa, A., Nishiyama, K., Sugano, Y., Mori, T., Dohmae, N., Hirata, K., Nakada-Nakura, Y., Maturana, A.D., Tanaka, Y., Mori, H., Sugita, Y., Arisaka, F., Ito, K., Ishitani, R., Tsukazaki, T., Nureki, O.(2014) Nature 509: 516-520
- PubMed: 24739968
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13167
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3WO6, 3WO7 - PubMed Abstract:
Newly synthesized membrane proteins must be accurately inserted into the membrane, folded and assembled for proper functioning. The protein YidC inserts its substrates into the membrane, thereby facilitating membrane protein assembly in bacteria; the homologous proteins Oxa1 and Alb3 have the same function in mitochondria and chloroplasts, respectively. In the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane, YidC functions as an independent insertase and a membrane chaperone in cooperation with the translocon SecYEG. Here we present the crystal structure of YidC from Bacillus halodurans, at 2.4 Å resolution. The structure reveals a novel fold, in which five conserved transmembrane helices form a positively charged hydrophilic groove that is open towards both the lipid bilayer and the cytoplasm but closed on the extracellular side. Structure-based in vivo analyses reveal that a conserved arginine residue in the groove is important for the insertion of membrane proteins by YidC. We propose an insertion mechanism for single-spanning membrane proteins, in which the hydrophilic environment generated by the groove recruits the extracellular regions of substrates into the low-dielectric environment of the membrane.
Organizational Affiliation:
1] Department of Biological Sciences, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan [2] Global Research Cluster, RIKEN, 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako-shi, Saitama 351-0198, Japan [3].