Complex Structure of the DNA-binding Domain of AdpA, the Global Transcription Factor in Streptomyces griseus, and a Target Duplex DNA Reveals the Structural Basis of Its Tolerant DNA Sequence Specificity
Yao, M.D., Ohtsuka, J., Nagata, K., Miyazono, K., Zhi, Y., Ohnishi, Y., Tanokura, M.(2013) J Biol Chem 288: 31019-31029
- PubMed: 24019524
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.473611
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3W6V - PubMed Abstract:
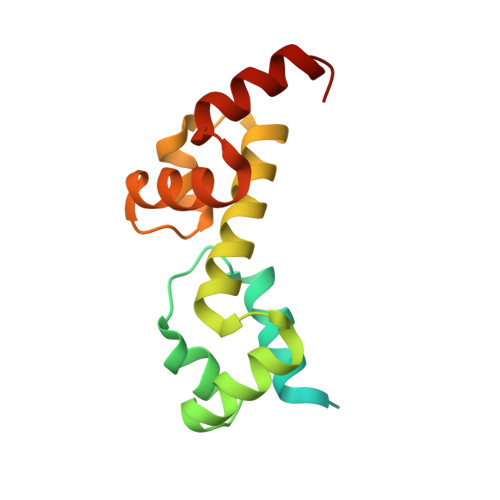
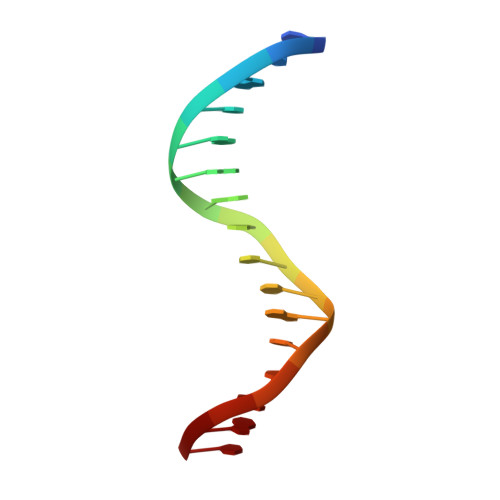
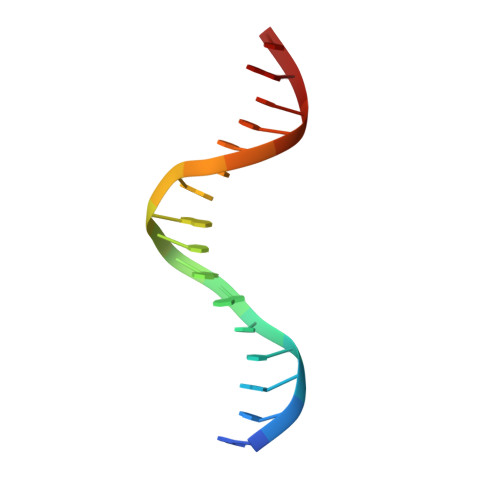
AdpA serves as the global transcription factor in the A-factor regulatory cascade, controlling the secondary metabolism and morphological differentiation of the filamentous bacterium Streptomyces griseus. AdpA binds to over 500 operator regions with the consensus sequence 5'-TGGCSNGWWY-3' (where S is G or C, W is A or T, Y is T or C, and N is any nucleotide). However, it is still obscure how AdpA can control hundreds of genes. To elucidate the structural basis of this tolerant DNA recognition by AdpA, we focused on the interaction between the DNA-binding domain of AdpA (AdpA-DBD), which consists of two helix-turn-helix motifs, and a target duplex DNA containing the consensus sequence 5'-TGGCGGGTTC-3'. The crystal structure of the AdpA-DBD-DNA complex and the mutant analysis of AdpA-DBD revealed its unique manner of DNA recognition, whereby only two arginine residues directly recognize the consensus sequence, explaining the strict recognition of G and C at positions 2 and 4, respectively, and the tolerant recognition of other positions of the consensus sequence. AdpA-DBD confers tolerant DNA sequence specificity to AdpA, allowing it to control hundreds of genes as a global transcription factor.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Departments of Applied Biological Chemistry and.