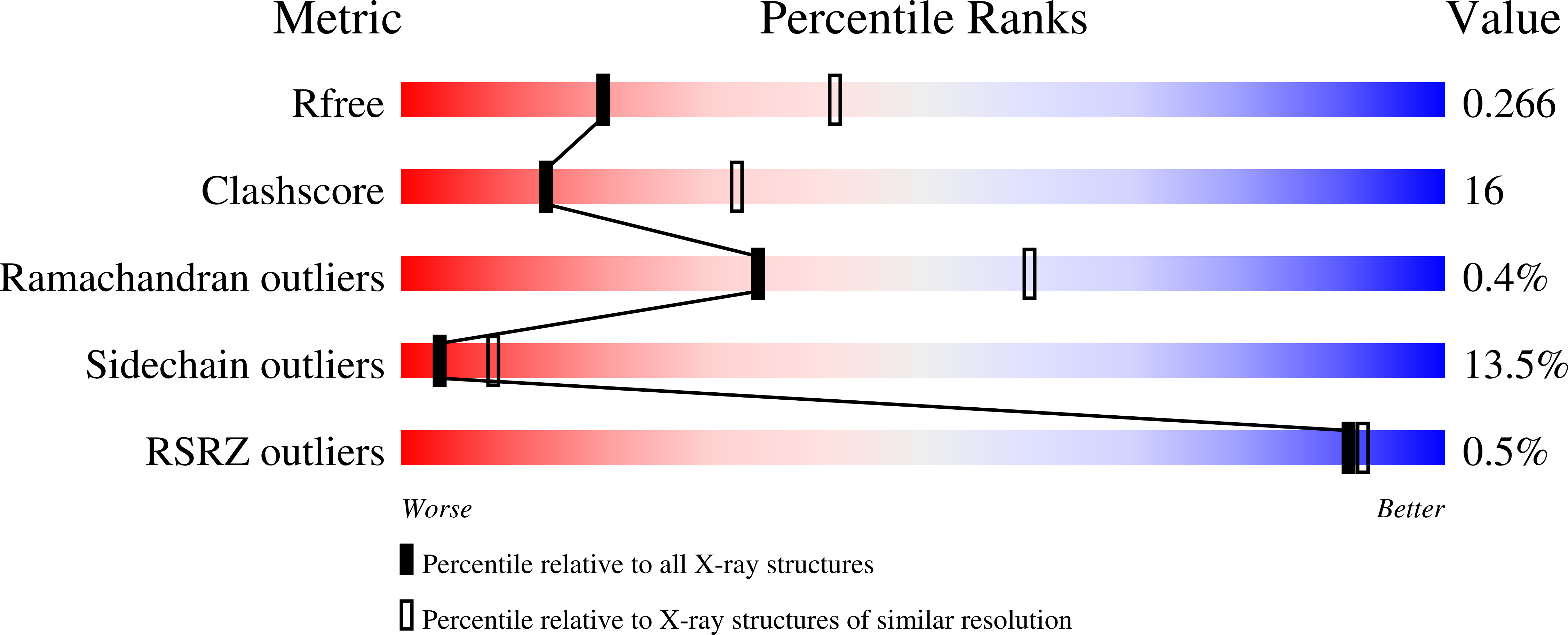
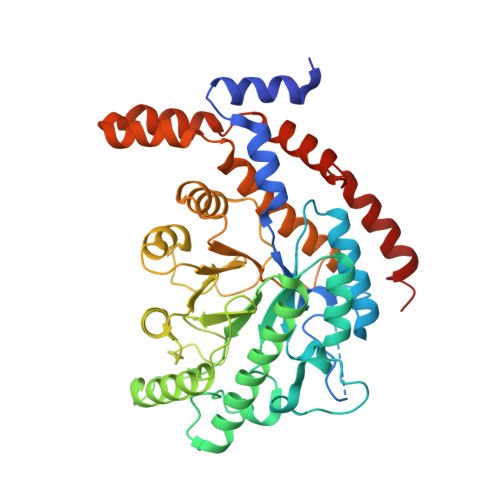
Structure-based studies on the metal binding of two-metal-dependent sugar isomerases.
Prabhu, P., Doan, T.N., Tiwari, M., Singh, R., Kim, S.C., Hong, M.K., Kang, Y.C., Kang, L.W., Lee, J.K.(2014) FEBS J 281: 3446-3459
- PubMed: 24925069
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.12872
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3P14, 3UU0, 3UVA, 3UXI - PubMed Abstract:
Two-metal-dependent sugar isomerases are important in the synthesis of rare sugars. Many of their properties, specifically their metal dependency, have not been sufficiently explored. Here we used X-ray crystallography, site-directed mutagenesis, isothermal titration calorimetry and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy to investigate the molecular determinants of the metal-binding affinity of l-rhamnose isomerase, a two-Mn(2+) -dependent isomerase from Bacillus halodurans (BHRI). The crystal structure of BHRI confirmed the presence of two metal ion-binding sites: a structural metal ion-binding site for substrate binding, and a catalytic metal ion-binding site that catalyzes a hydride shift. One conserved amino acid, W38, in wild-type BHRI was identified as a critical residue for structural Mn(2+) binding and thus the catalytic efficiency of BHRI. This function of W38 was explored by replacing it with other amino acids. Substitution by Phe, His, Lys, Ile or Ala caused complete loss of catalytic activity. The role of W38 was further examined by analyzing the crystal structure of wild-type BHRI and two inactive mutants of BHRI (W38F and W38A) in complex with Mn(2+) . A structural comparison of the mutants and the wild-type revealed differences in their coordination of Mn(2+) , including changes in metal-ligand bond length and affinity for Mn(2+) . The role of W38 was further confirmed in another two-metal-dependent enzyme: xylose isomerase from Bacillus licheniformis. These data suggest that W38 stabilizes protein-metal complexes and in turn assists ligand binding during catalysis in two-metal-dependent isomerases. BHRI and BHRI bind by x-ray crystallography (View interaction).
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Konkuk University, Seoul, Korea.