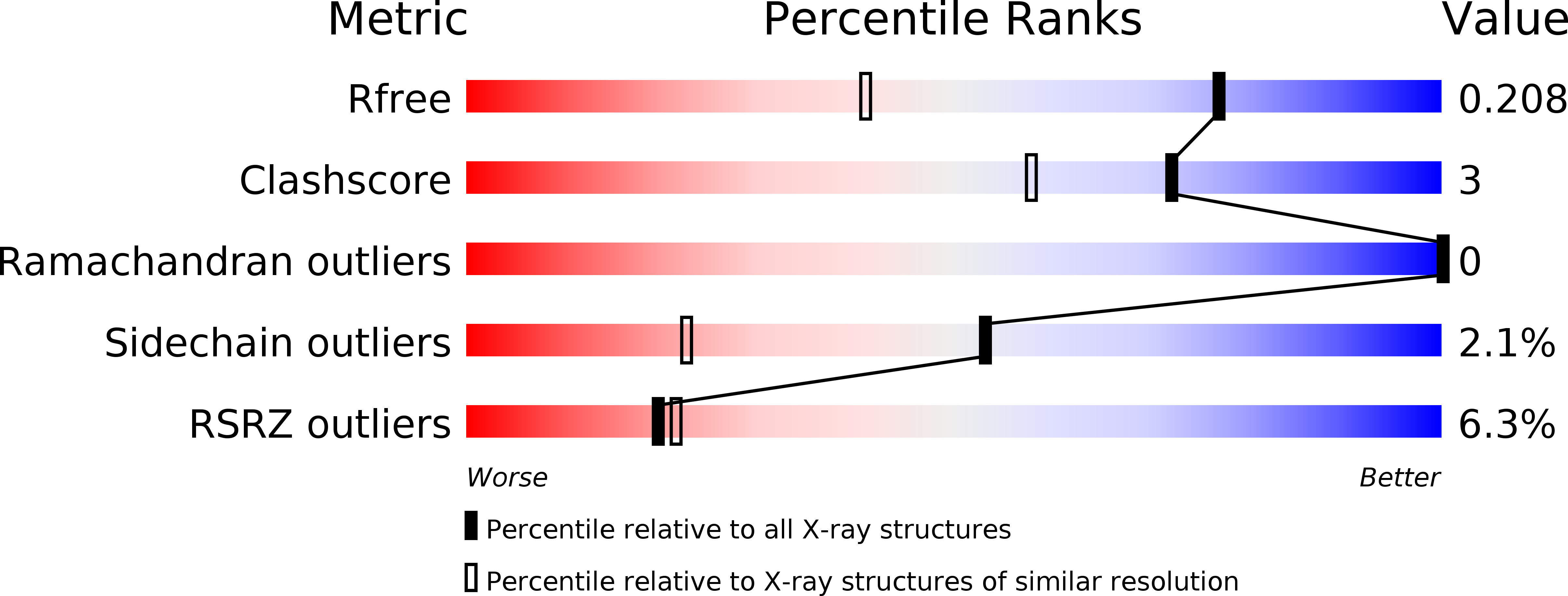
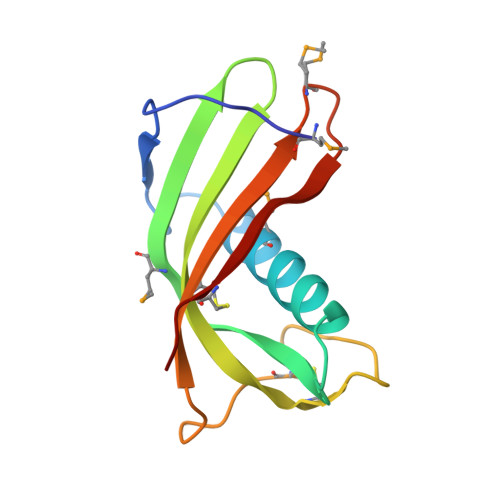
The crystal structures of two salivary cystatins from the tick Ixodes scapularis and the effect of these inhibitors on the establishment of Borrelia burgdorferi infection in a murine model.
Kotsyfakis, M., Horka, H., Salat, J., Andersen, J.F.(2010) Mol Microbiol 77: 456-470
- PubMed: 20545851
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07220.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3LH4, 3MWZ, 4ZM8 - PubMed Abstract:
We have previously demonstrated that two salivary cysteine protease inhibitors from the Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease) vector Ixodes scapularis- namely sialostatins L and L2 - play an important role in tick biology, as demonstrated by the fact that silencing of both sialostatins in tandem results in severe feeding defects. Here we show that sialostatin L2 - but not sialostatin L - facilitates the growth of B. burgdorferi in murine skin. To examine the structural basis underlying these differential effects of the two sialostatins, we have determined the crystal structures of both sialostatin L and L2. This is the first structural analysis of cystatins from an invertebrate source. Sialostatin L2 crystallizes as a monomer with an 'unusual' conformation of the N-terminus, while sialostatin L crystallizes as a domain-swapped dimer with an N-terminal conformation similar to other cystatins. Deletion of the 'unusual' N-terminal five residues of sialostatin L2 results in marked changes in its selectivity, suggesting that this region is a particularly important determinant of the biochemical activity of sialostatin L2. Collectively, our results reveal the structure of two tick salivary components that facilitate vector blood feeding and that one of them also supports pathogen transmission to the vertebrate host.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Genomics and Proteomics of Disease Vectors, Institute of Parasitology, Biology Centre of the Academy of Sciences of Czech Republic, Ceske Budejovice, Czech Republic.