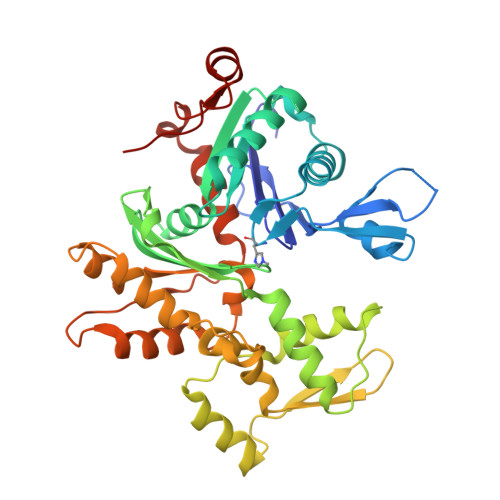
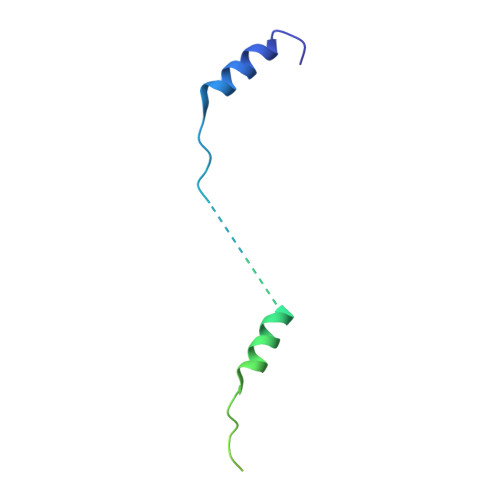
Structure of a longitudinal actin dimer assembled by tandem w domains: implications for actin filament nucleation.
Rebowski, G., Namgoong, S., Boczkowska, M., Leavis, P.C., Navaza, J., Dominguez, R.(2010) J Mol Biol 403: 11-23
- PubMed: 20804767
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2010.08.040
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3M1F, 3M3N - PubMed Abstract:
Actin filament nucleators initiate polymerization in cells in a regulated manner. A common architecture among these molecules consists of tandem WASP homology 2 domains (W domains) that recruit three to four actin subunits to form a polymerization nucleus. We describe a low-resolution crystal structure of an actin dimer assembled by tandem W domains, where the first W domain is cross-linked to Cys374 of the actin subunit bound to it, whereas the last W domain is followed by the C-terminal pointed end-capping helix of thymosin β4. While the arrangement of actin subunits in the dimer resembles that of a long-pitch helix of the actin filament, important differences are observed. These differences result from steric hindrance of the W domain with intersubunit contacts in the actin filament. We also determined the structure of the first W domain of Vibrio parahaemolyticus VopL cross-linked to actin Cys374 and show it to be nearly identical with non-cross-linked W-Actin structures. This result validates the use of cross-linking as a tool for the study of actin nucleation complexes, whose natural tendency to polymerize interferes with most structural methods. Combined with a biochemical analysis of nucleation, the structures may explain why nucleators based on tandem W domains with short inter-W linkers have relatively weak activity, cannot stay bound to filaments after nucleation, and are unlikely to influence filament elongation. The findings may also explain why nucleation-promoting factors of the Arp2/3 complex, which are related to tandem-W-domain nucleators, are ejected from branch junctions after nucleation. We finally show that the simple addition of the C-terminal pointed end-capping helix of thymosin β4 to tandem W domains can change their activity from actin filament nucleation to monomer sequestration.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Physiology, University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, 3700 Hamilton Walk, Philadelphia, PA 19104-6085, USA.