Mouse Apom Displays an Unprecedented Seven-Stranded Lipocalin Fold: Folding Decoy or Alternative Native Fold?
Sevvana, M., Kassler, K., Ahnstrom, J., Weiler, S., Dahlback, B., Sticht, H., Muller, Y.A.(2010) J Mol Biol 404: 363
- PubMed: 20932978
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2010.09.062
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2XKL - PubMed Abstract:
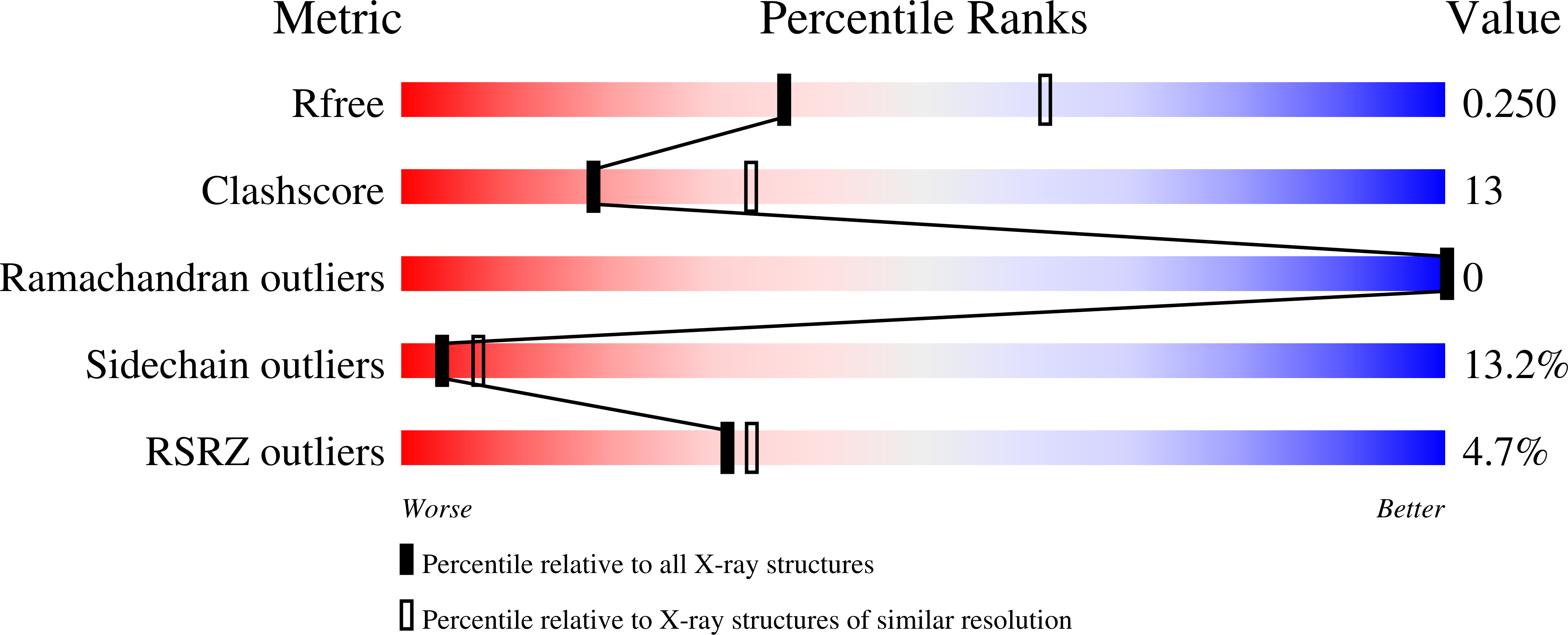
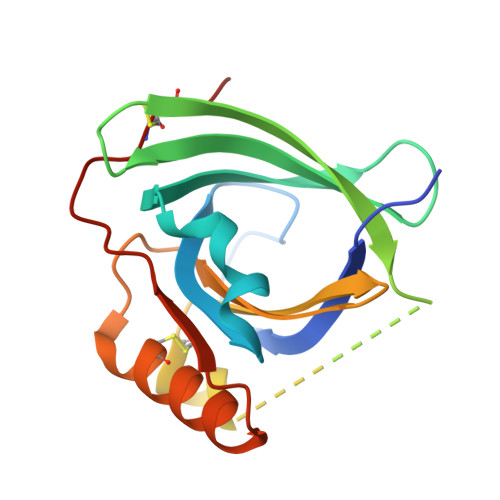
Mouse apolipoprotein M (m-apoM) displays a 79% sequence identity to human apolipoprotein M (h-apoM). Both proteins are apolipoproteins associated with high-density lipoproteins, with similar anticipated biological functions. The structure of h-apoM has recently been determined by X-ray crystallography, which revealed that h-apoM displays, as expected, a lipocalin-like fold characterized by an eight-stranded β‑barrel that encloses an internal fatty-acid-binding site. Surprisingly, this is not true for m-apoM. After refolding from inclusion bodies, the crystal structure of m-apoM (reported here at 2.5 Å resolution) displays a novel yet unprecedented seven-stranded β-barrel structure. The fold difference is not caused by a mere deletion of a single β-strand; instead, β-strands E and F are removed and replaced by a single β-strand A' formed from residues from the N-terminus. Molecular dynamics simulations suggest that m-apoM is able to adopt both a seven-stranded barrel structure and an eight-stranded barrel structure in solution, and that both folds are comparably stable. Thermal unfolding simulations identify the position where β-strand exchange occurs as the weak point of the β-barrel. We wonder whether the switch in topology could have a biological function and could facilitate ligand release, since it goes hand in hand with a narrowing of the barrel diameter. Possibly also, the observed conformation represents an on-pathway or off-pathway folding intermediate of apoM. The difference in fold topology is quite remarkable, and the fold promiscuity observed for m-apoM might possibly provide a glimpse at potential cross-points during the evolution of β-barrels.
Organizational Affiliation:
Lehrstuhl für Biotechnik, Department Biologie, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Im IZMP, Henkestr. 91, D-91052 Erlangen, Germany.