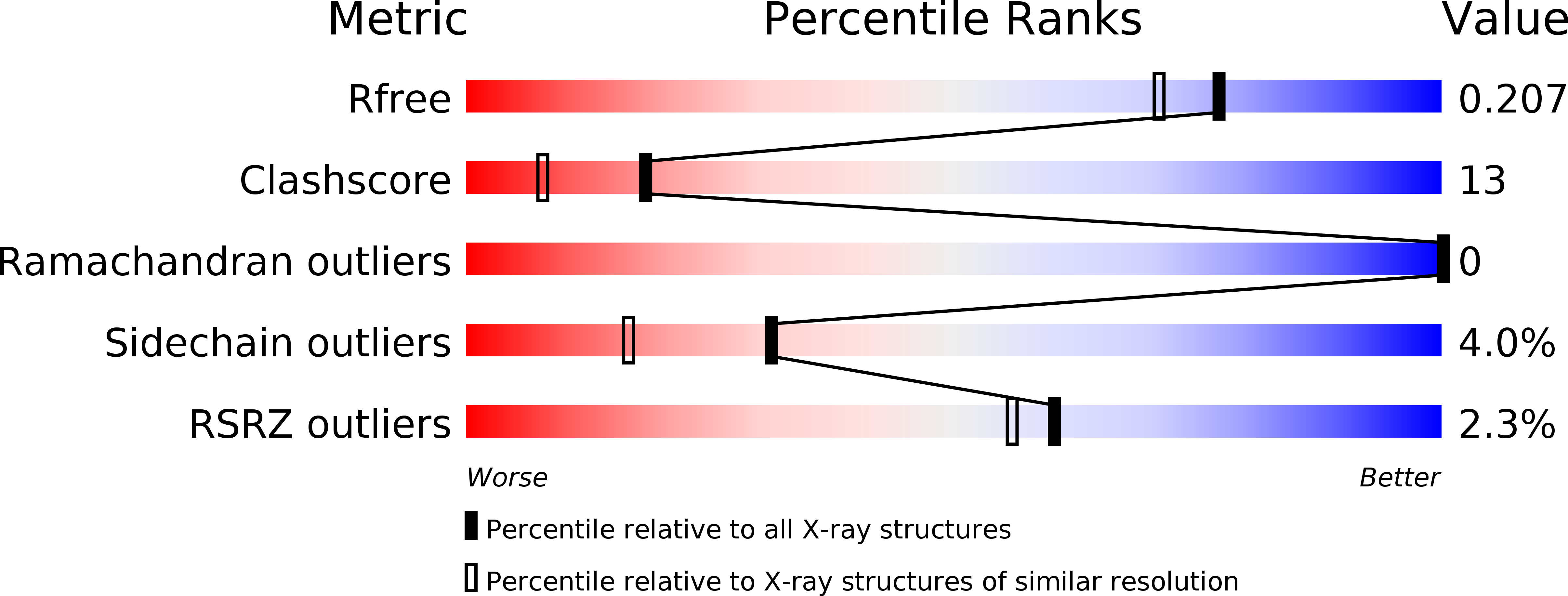
Structural Insights into the Interaction of the Nip7 PUA Domain with Polyuridine RNA
Coltri, P.P., Guimaraes, B.G., Granato, D.C., Luz, J.S., Teixeira, E.C., Oliveira, C.C., Zanchin, N.I.(2007) Biochemistry 46: 14177-14187
- PubMed: 18001138
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi7015876
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2P38 - PubMed Abstract:
The conserved protein Nip7 is involved in ribosome biogenesis, being required for proper 27S pre-rRNA processing and 60S ribosome subunit assembly in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast Nip7p interacts with nucleolar proteins and with the exosome subunit Rrp43p, but its molecular function remains to be determined. Solution of the Pyrococcus abyssi Nip7 (PaNip7) crystal structure revealed a monomeric protein composed by two alpha-beta domains. The N-terminal domain is formed by a five-stranded antiparallel beta-sheet surrounded by three alpha-helices and a 310 helix while the C-terminal, a mixed beta-sheet domain composed by strands beta8 to beta12, one alpha-helix, and a 310 helix, corresponds to the conserved PUA domain (after Pseudo-Uridine synthases and Archaeosine-specific transglycosylases). By combining structural analyses and RNA interaction assays, we assessed the ability of both yeast and archaeal Nip7 orthologues to interact with RNA. Structural alignment of the PaNip7 PUA domain with the RNA-interacting surface of the ArcTGT (archaeosine tRNA-guanine transglycosylase) PUA domain indicated that in the archaeal PUA domain positively charged residues (R151, R152, K155, and K158) are involved in RNA interaction. However, equivalent positions are occupied by mostly hydrophobic residues (A/G160, I161, F164, and A167) in eukaryotic Nip7 orthologues. Both proteins can bind specifically to polyuridine, and RNA interaction requires specific residues of the PUA domain as determined by site-directed mutagenesis. This work provides experimental verification that the PUA domain mediates Nip7 interaction with RNA and reveals that the preference for interaction with polyuridine sequences is conserved in Archaea and eukaryotic Nip7 proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Center for Structural Molecular Biology, Brazilian Synchrotron Light Laboratory, LNLS, Rua Giuseppe Maximo Scolfaro 10000, P.O. Box 6192, CEP13083-970, Campinas SP, Brazil.