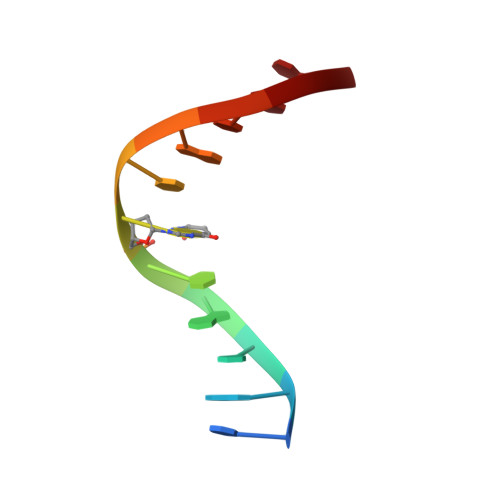
Solution structure of DNA containing alpha-OH-PdG: the mutagenic adduct produced by acrolein.
Zaliznyak, T., Bonala, R., Attaluri, S., Johnson, F., de los Santos, C.(2009) Nucleic Acids Res 37: 2153-2163
- PubMed: 19223332
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp076
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2KD9, 2KDA - PubMed Abstract:
Acrolein is a cell metabolic product and a main component of cigarette smoke. Its reaction with DNA produces two guanine lesions gamma-OH-PdG, a major adduct that is nonmutagenic in mammalian cells, and the positional isomer alpha-OH-PdG. We describe here the solution structure of a short DNA duplex containing a single alpha-OH-PdG lesion, as determined by solution NMR spectroscopy and restrained molecular dynamics simulations. The spectroscopic data show a mostly regular right-handed helix, locally perturbed at its center by the presence of the lesion. All undamaged residues of the duplex are in anti orientation, forming standard Watson-Crick base-pair alignments. Duplication of proton signals near the damaged site differentiates two enantiomeric duplexes, thus establishing the exocyclic nature of the lesion. At the lesion site, alpha-OH-PdG rotates to a syn conformation, pairing to its counter cytosine residue that is protonated at pH 5.9. Three-dimensional models produced by restrained molecular dynamics simulations show different hydrogen-bonding patterns between the lesion and its cytosine partner and identify further stabilization of alpha-OH-PdG in a syn conformation by intra-residue hydrogen bonds. We compare the alpha-OH-PdG.dC duplex structure with that of duplexes containing the analogous lesion propano-dG and discuss the implications of our findings for the mutagenic bypass of acrolein lesions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Pharmacological Sciences, Stony Brook University, School of Medicine Stony Brook, NY 11794-8651, USA.