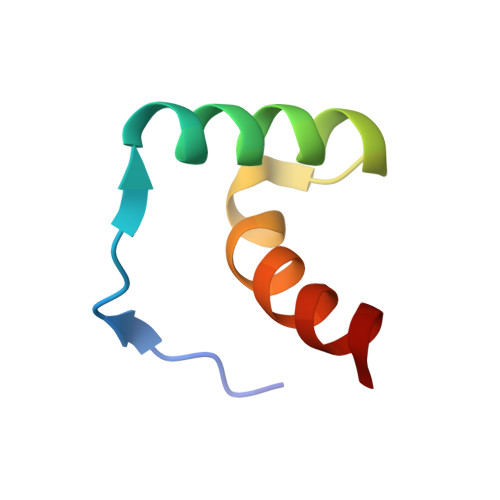
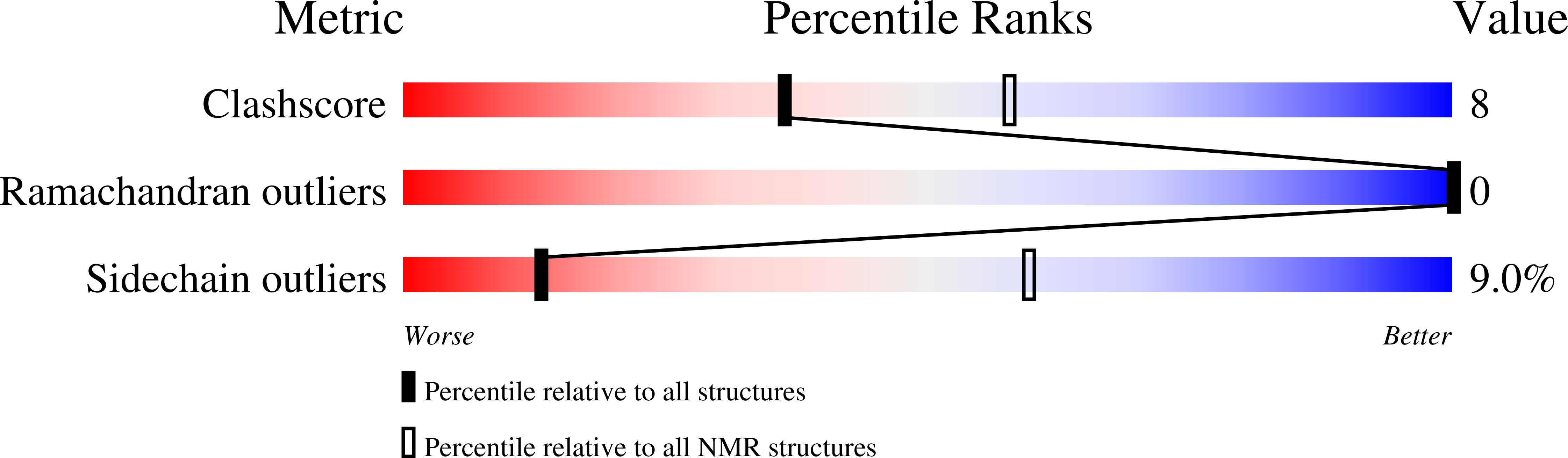Solution structure of the Pseudomonas putida protein PpPutA45 and its DNA complex
Halouska, S., Zhou, Y., Becker, D.F., Powers, R.(2008) Proteins 75: 12-27
- PubMed: 18767154
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.22217
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2JXG, 2JXH, 2JXI - PubMed Abstract:
Proline utilization A (PutA) is a membrane-associated multifunctional enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of proline to glutamate in a two-step process. In certain, gram-negative bacteria such as Pseudomonas putida, PutA also acts as an auto repressor in the cytoplasm, when an insufficient concentration of proline is available. Here, the N-terminal residues 1-45 of PutA from P. putida (PpPutA45) are shown to be responsible for DNA binding and dimerization. The solution structure of PpPutA45 was determined using NMR methods, where the protein is shown to be a symmetrical homodimer (12 kDa) consisting of two ribbon-helix-helix (RHH) structures. DNA sequence recognition by PpPutA45 was determined using DNA gel mobility shift assays and NMR chemical shift perturbations (CSPs). PpPutA45 was shown to bind a 14 base-pair DNA oligomer (5'-GCGGTTGCACCTTT-3'). A model of the PpPutA45-DNA oligomer complex was generated using Haddock 2.1. The antiparallel beta-sheet that results from PpPutA45 dimerization serves as the DNA recognition binding site by inserting into the DNA major groove. The dimeric core of four alpha-helices provides a structural scaffold for the beta-sheet from which residues Thr5, Gly7, and Lys9 make sequence-specific contacts with the DNA. The structural model implies flexibility of Lys9 which can make hydrogen bond contacts with either guanine or thymine. The high sequence and structure conservation of the PutA RHH domain suggest interdomain interactions play an important role in the evolution of the protein.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln, Nebraska 68588, USA.