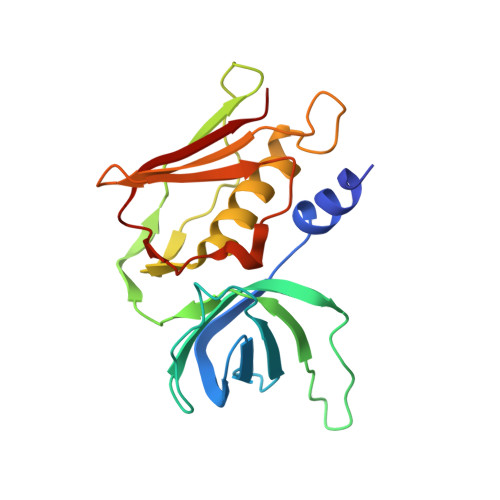
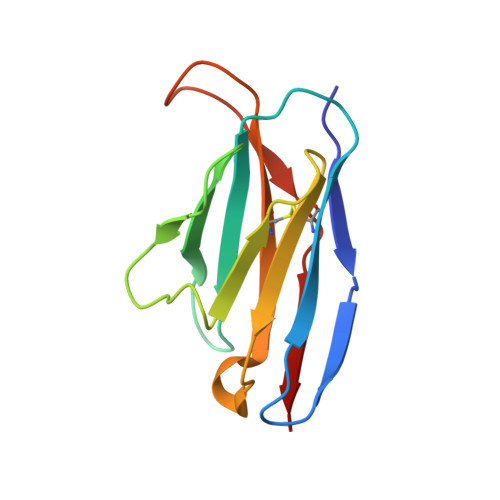
Structural basis of T-cell specificity and activation by the bacterial superantigen TSST-1.
Moza, B., Varma, A.K., Buonpane, R.A., Zhu, P., Herfst, C.A., Nicholson, M.J., Wilbuer, A.K., Seth, N.P., Wucherpfennig, K.W., McCormick, J.K., Kranz, D.M., Sundberg, E.J.(2007) EMBO J 26: 1187-1197
- PubMed: 17268555
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601531
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2IJ0 - PubMed Abstract:
Superantigens (SAGs) bind simultaneously to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) and T-cell receptor (TCR) molecules, resulting in the massive release of inflammatory cytokines that can lead to toxic shock syndrome (TSS) and death. A major causative agent of TSS is toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1), which is unique relative to other bacterial SAGs owing to its structural divergence and its stringent TCR specificity. Here, we report the crystal structure of TSST-1 in complex with an affinity-matured variant of its wild-type TCR ligand, human T-cell receptor beta chain variable domain 2.1. From this structure and a model of the wild-type complex, we show that TSST-1 engages TCR ligands in a markedly different way than do other SAGs. We provide a structural basis for the high TCR specificity of TSST-1 and present a model of the TSST-1-dependent MHC-SAG-TCR T-cell signaling complex that is structurally and energetically unique relative to those formed by other SAGs. Our data also suggest that protein plasticity plays an exceptionally significant role in this affinity maturation process that results in more than a 3000-fold increase in affinity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Boston Biomedical Research Institute, Watertown, MA 02472, USA.