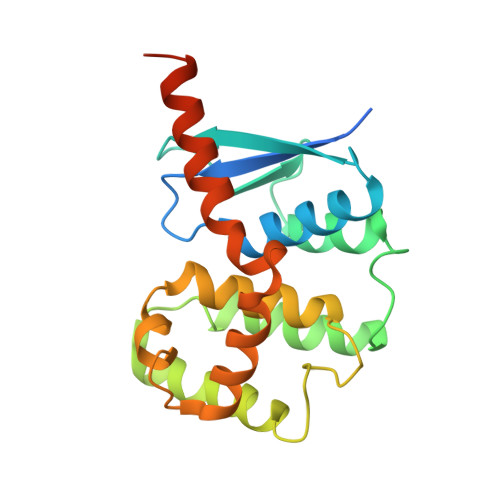
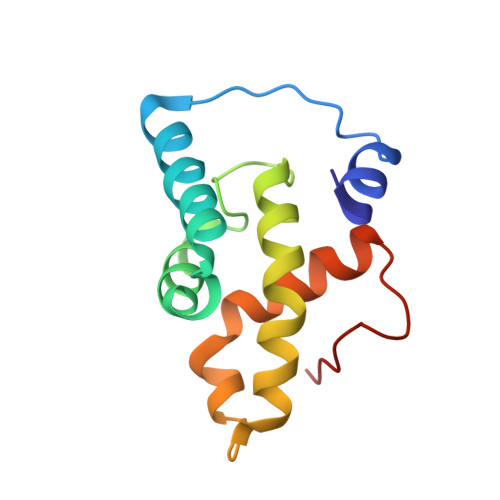
Structural basis of yeast aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase complex formation revealed by crystal structures of two binary sub-complexes.
Simader, H., Hothorn, M., Kohler, C., Basquin, J., Simos, G., Suck, D.(2006) Nucleic Acids Res 34: 3968-3979
- PubMed: 16914447
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl560
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2HRK, 2HSM, 2HSN - PubMed Abstract:
The yeast aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS) complex is formed by the methionyl- and glutamyl-tRNA synthetases (MetRS and GluRS, respectively) and the tRNA aminoacylation cofactor Arc1p. It is considered an evolutionary intermediate between prokaryotic aaRS and the multi- aaRS complex found in higher eukaryotes. While a wealth of structural information is available on the enzymatic domains of single aaRS, insight into complex formation between eukaryotic aaRS and associated protein cofactors is missing. Here we report crystal structures of the binary complexes between the interacting domains of Arc1p and MetRS as well as those of Arc1p and GluRS at resolutions of 2.2 and 2.05 A, respectively. The data provide a complete structural model for ternary complex formation between the interacting domains of MetRS, GluRS and Arc1p. The structures reveal that all three domains adopt a glutathione S-transferase (GST)-like fold and that simultaneous interaction of Arc1p with GluRS and MetRS is mediated by the use of a novel interface in addition to a classical GST dimerization interaction. The results demonstrate a novel role for this fold as a heteromerization domain specific to eukaryotic aaRS, associated proteins and protein translation elongation factors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural and Computational Biology Unit, European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), Meyerhofstrasse 1, D-69117 Heidelberg, Germany.