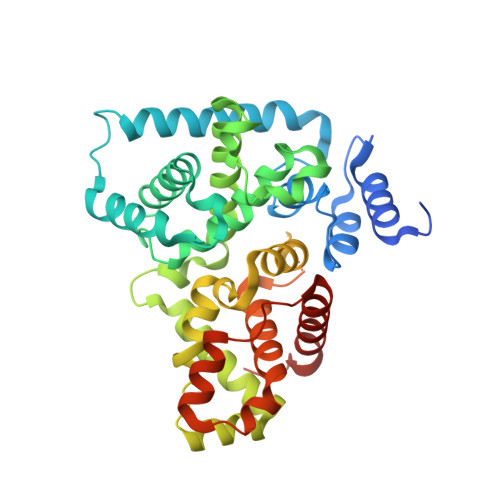
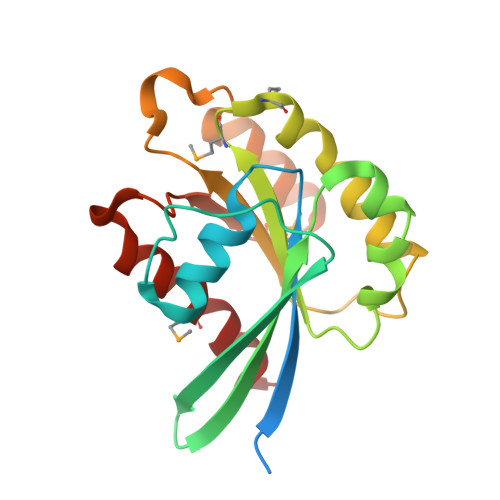
TBC-domain GAPs for Rab GTPases accelerate GTP hydrolysis by a dual-finger mechanism.
Pan, X., Eathiraj, S., Munson, M., Lambright, D.G.(2006) Nature 442: 303-306
- PubMed: 16855591
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04847
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2G77 - PubMed Abstract:
Rab GTPases regulate membrane trafficking by cycling between inactive (GDP-bound) and active (GTP-bound) conformations. The duration of the active state is limited by GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs), which accelerate the slow intrinsic rate of GTP hydrolysis. Proteins containing TBC (Tre-2, Bub2 and Cdc16) domains are broadly conserved in eukaryotic organisms and function as GAPs for Rab GTPases as well as GTPases that control cytokinesis. An exposed arginine residue is a critical determinant of GAP activity in vitro and in vivo. It has been expected that the catalytic mechanism of TBC domains would parallel that of Ras and Rho family GAPs. Here we report crystallographic, mutational and functional analyses of complexes between Rab GTPases and the TBC domain of Gyp1p. In the crystal structure of a TBC-domain-Rab-GTPase-aluminium fluoride complex, which approximates the transition-state intermediate for GTP hydrolysis, the TBC domain supplies two catalytic residues in trans, an arginine finger analogous to Ras/Rho family GAPs and a glutamine finger that substitutes for the glutamine in the DxxGQ motif of the GTPase. The glutamine from the Rab GTPase does not stabilize the transition state as expected but instead interacts with the TBC domain. Strong conservation of both catalytic fingers indicates that most TBC-domain GAPs may accelerate GTP hydrolysis by a similar dual-finger mechanism.
Organizational Affiliation:
Program in Molecular Medicine & Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Pharmacology, UMASS Medical School, Two Biotech, 373 Plantation Street, Worcester, Massachusetts 01605, USA.