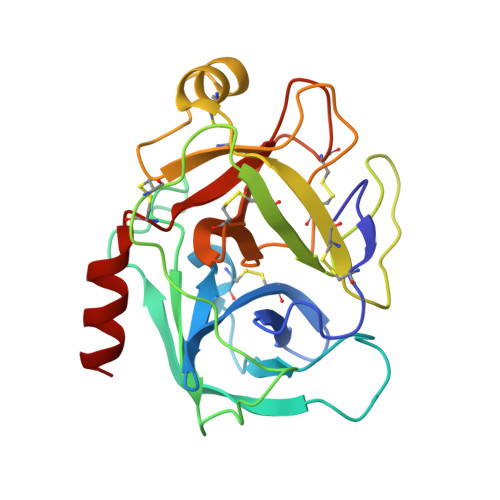
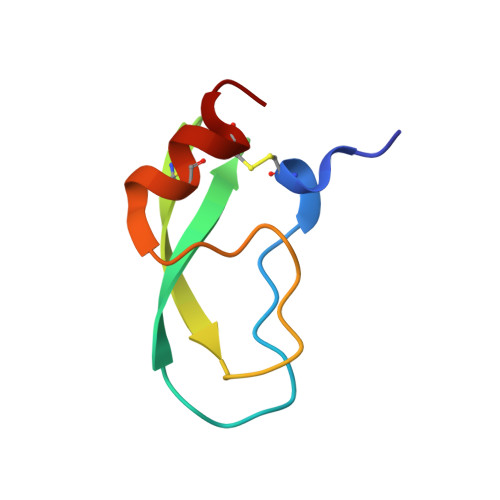
Functional and structural roles of the Cys14-Cys38 disulfide of bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor.
Zakharova, E., Horvath, M.P., Goldenberg, D.P.(2008) J Mol Biol 382: 998-1013
- PubMed: 18692070
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2008.07.063
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2FI3, 2FI4, 2FI5 - PubMed Abstract:
The disulfide bond between Cys14 and Cys38 of bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor lies on the surface of the inhibitor and forms part of the protease-binding region. The functional properties of three variants lacking this disulfide, with one or both of the Cys residues replaced with Ser, were examined, and X-ray crystal structures of the complexes with bovine trypsin were determined and refined to the 1.58-A resolution limit. The crystal structure of the complex formed with the mutant with both Cys residues replaced was nearly identical with that of the complex containing the wild-type protein, with the Ser oxygen atoms positioned to replace the disulfide bond with a hydrogen bond. The two structures of the complexes with single replacements displayed small local perturbations with alternate conformations of the Ser side chains. Despite the absence of the disulfide bond, the crystallographic temperature factors show no evidence of increased flexibility in the complexes with the mutant inhibitors. All three of the variants were cleaved by trypsin more rapidly than the wild-type inhibitor, by as much as 10,000-fold, indicating that the covalent constraint normally imposed by the disulfide contributes to the remarkable resistance to hydrolysis displayed by the wild-type protein. The rates of hydrolysis display an unusual dependence on pH over the range of 3.5-8.0, decreasing at the more alkaline values, as compared with the increased hydrolysis rates for normal substrates under these conditions. These observations can be accounted for by a model for inhibition in which an acyl-enzyme intermediate forms at a significant rate but is rapidly converted back to the enzyme-inhibitor complex by nucleophilic attack by the newly created amino group. The model suggests that a lack of flexibility in the acyl-enzyme intermediate, rather than the enzyme-inhibitor complex, may be a key factor in the ability of bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor and similar inhibitors to resist hydrolysis.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biology, University of Utah, 257 South 1400 East, Salt Lake City, UT 84112-0840, USA.