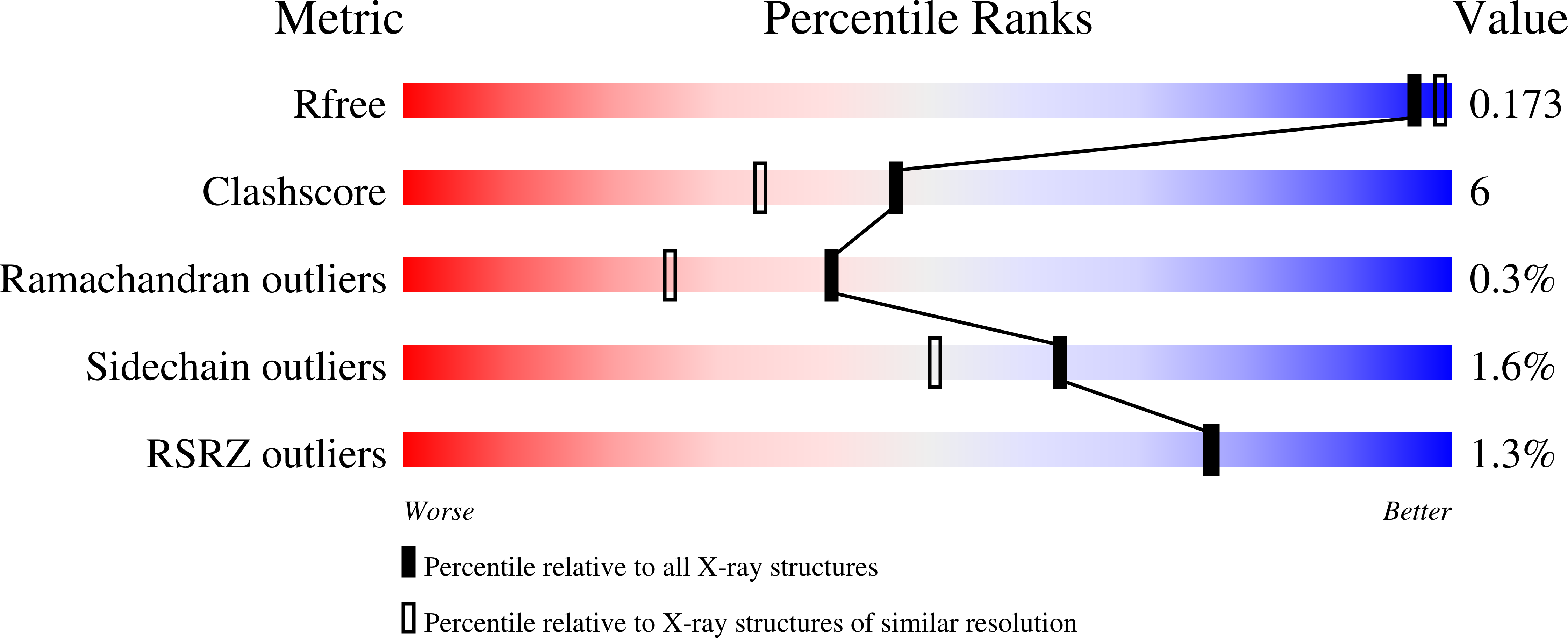
Understanding How Diverse -Mannanases Recognise Heterogeneous Substrates.
Tailford, L.E., Ducros, V.M.A., Flint, J.E., Roberts, S.M., Morland, C., Zechel, D.L., Smith, N., Bjornvad, M.E., Borchert, T.V., Wilson, K.S., Davies, G.J., Gilbert, H.J.(2009) Biochemistry 48: 7009
- PubMed: 19441796
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi900515d
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2WHJ, 2WHK, 2WHL, 2WHM - PubMed Abstract:
The mechanism by which polysaccharide-hydrolyzing enzymes manifest specificity toward heterogeneous substrates, in which the sequence of sugars is variable, is unclear. An excellent example of such heterogeneity is provided by the plant structural polysaccharide glucomannan, which comprises a backbone of beta-1,4-linked glucose and mannose units. beta-Mannanases, located in glycoside hydrolase (GH) families 5 and 26, hydrolyze glucomannan by cleaving the glycosidic bond of mannosides at the -1 subsite. The mechanism by which these enzymes select for glucose or mannose at distal subsites, which is critical to defining their substrate specificity on heterogeneous polymers, is currently unclear. Here we report the biochemical properties and crystal structures of both a GH5 mannanase and a GH26 mannanase and describe the contributions to substrate specificity in these enzymes. The GH5 enzyme, BaMan5A, derived from Bacillus agaradhaerens, can accommodate glucose or mannose at both its -2 and +1 subsites, while the GH26 Bacillus subtilis mannanase, BsMan26A, displays tight specificity for mannose at its negative binding sites. The crystal structure of BaMan5A reveals that a polar residue at the -2 subsite can make productive contact with the substrate 2-OH group in either its axial (as in mannose) or its equatorial (as in glucose) configuration, while other distal subsites do not exploit the 2-OH group as a specificity determinant. Thus, BaMan5A is able to hydrolyze glucomannan in which the sequence of glucose and mannose is highly variable. The crystal structure of BsMan26A in light of previous studies on the Cellvibrio japonicus GH26 mannanases CjMan26A and CjMan26C reveals that the tighter mannose recognition at the -2 subsite is mediated by polar interactions with the axial 2-OH group of a (4)C(1) ground state mannoside. Mutagenesis studies showed that variants of CjMan26A, from which these polar residues had been removed, do not distinguish between Man and Glc at the -2 subsite, while one of these residues, Arg 361, confers the elevated activity displayed by the enzyme against mannooligosaccharides. The biological rationale for the variable recognition of Man- and Glc-configured sugars by beta-mannanases is discussed.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute for Cell and Molecular Biosciences, Newcastle University, The Medical School, Newcastle upon Tyne NE2 4HH, UK.