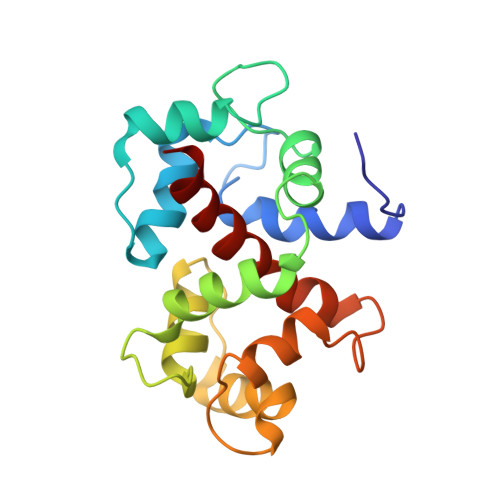
Solution structures of yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae calmodulin in calcium- and target peptide-bound states reveal similarities and differences to vertebrate calmodulin.
Ogura, K., Kumeta, H., Takahasi, K., Kobashigawa, Y., Yoshida, R., Itoh, H., Yazawa, M., Inagaki, F.(2012) Genes Cells 17: 159-172
- PubMed: 22280008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2443.2012.01580.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2LHH, 2LHI - PubMed Abstract:
We determined the solution structures of the calmodulin (CaM) isoform from yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yCaM) in the calcium-bound form and in complex with a target peptide using NMR spectroscopy and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). yCaM shows a number of unique features distinct from the vertebrate CaM isoforms: (i) it has only approximately 60% sequence identity to vertebrate CaM; (ii) its fourth Ca(2+)-binding domain is inactivated by amino acid substitution. As NMR analyses of Ca(2+)-bound full-length yCaM implied that the fourth EF-hand motif region (EF4) presents a disordered conformation, we determined the solution structure of an EF4-deletion mutant of Ca(2+)-bound yCaM. The deletion mutant showed a compact globular structure, with the target recognition sites of the N-terminal domain and the third EF-hand region bound to each other. Furthermore, we determined the solution structure of Ca(2+)-bound yCaM complexed with a calcineurin-derived peptide. Interestingly, the structure closely resembled that of the vertebrate CaM-calcineurin complex, with the EF4 region in cooperation with the peptide binding. Moreover, the results of SAXS analyses were consistent with the NMR solution structures and showed the conformational changes of yCaM in three functional stages. These unique structural characteristics of yCaM are closely related to Ca(2+)-mediated signal transduction in yeast.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Structural Biology, Faculty of Advanced Life Science, Hokkaido University, Kita 21 Nishi 11, Kita-ku, Sapporo 001-0021, Japan.