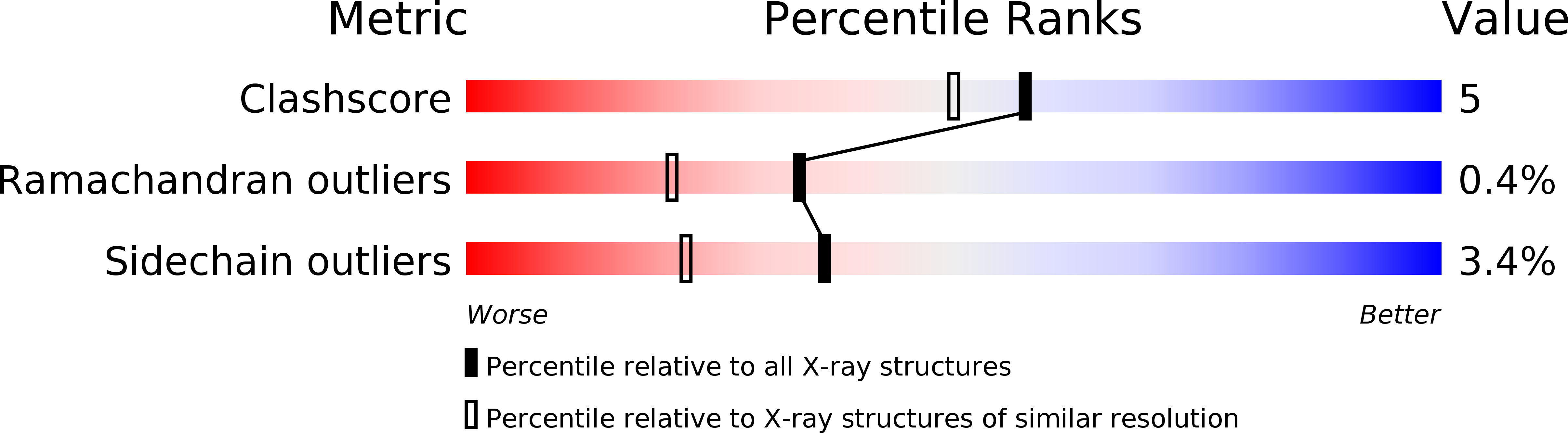
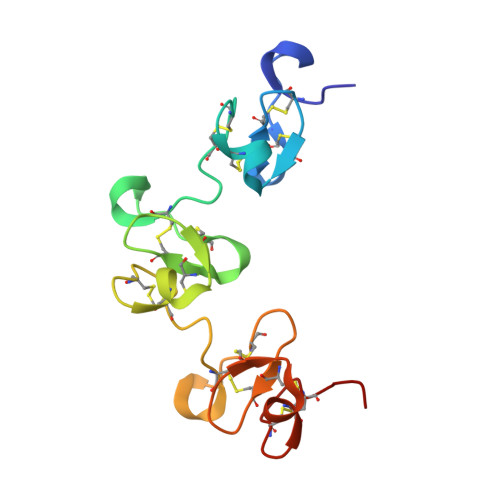
Similarity between protein-protein and protein-carbohydrate interactions, revealed by two crystal structures of lectins from the roots of pokeweed.
Hayashida, M., Fujii, T., Hamasu, M., Ishiguro, M., Hata, Y.(2003) J Mol Biol 334: 551-565
- PubMed: 14623194
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2003.09.076
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1ULK, 1ULM - PubMed Abstract:
The roots of pokeweed (Phytolacca americana) are known to contain the lectins designated PL-A, PL-B, PL-C, PL-D1, and PL-D2. Of these lectins, the crystal structures of two PLs, the ligand-free PL-C and the complex of PL-D2 with tri-N-acetylchitotriose, have been determined at 1.8A resolution. The polypeptide chains of PL-C and PL-D2 form three and two repetitive chitin-binding domains, respectively. In the crystal structure of the PL-D2 complex, one trisaccharide molecule is shared mainly between two neighboring molecules related to each other by a crystallographic 2(1)-screw axis, and infinite helical chains of complexed molecules are generated by the sharing of ligand molecules. The crystal structure of PL-C reveals that the molecule is a dimer of two identical subunits, whose polypeptide chains are located in a head-to-tail fashion by a molecular 2-fold axis. Three putative carbohydrate-binding sites in each subunit are located in the dimer interface. The dimerization of PL-C is performed through the hydrophobic interactions between the carbohydrate-binding sites of the opposite domains in the dimer, leading to a distinct dimerization mode from that of wheat-germ agglutinin. Three aromatic residues in each carbohydrate-binding site of PL-C are involved in the dimerization. These residues correspond to the residues that interact mainly with the trisaccharide in the PL-D2 complex and appear to mimic the saccharide residues in the complex. Consequently, the present structure of the PL-C dimer has no room for accommodating carbohydrate. The quaternary structure of PL-C formed through these putative carbohydrate-binding residues may lead to the lack of hemagglutinating activity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University, Uji, 611-0011, Kyoto, Japan.