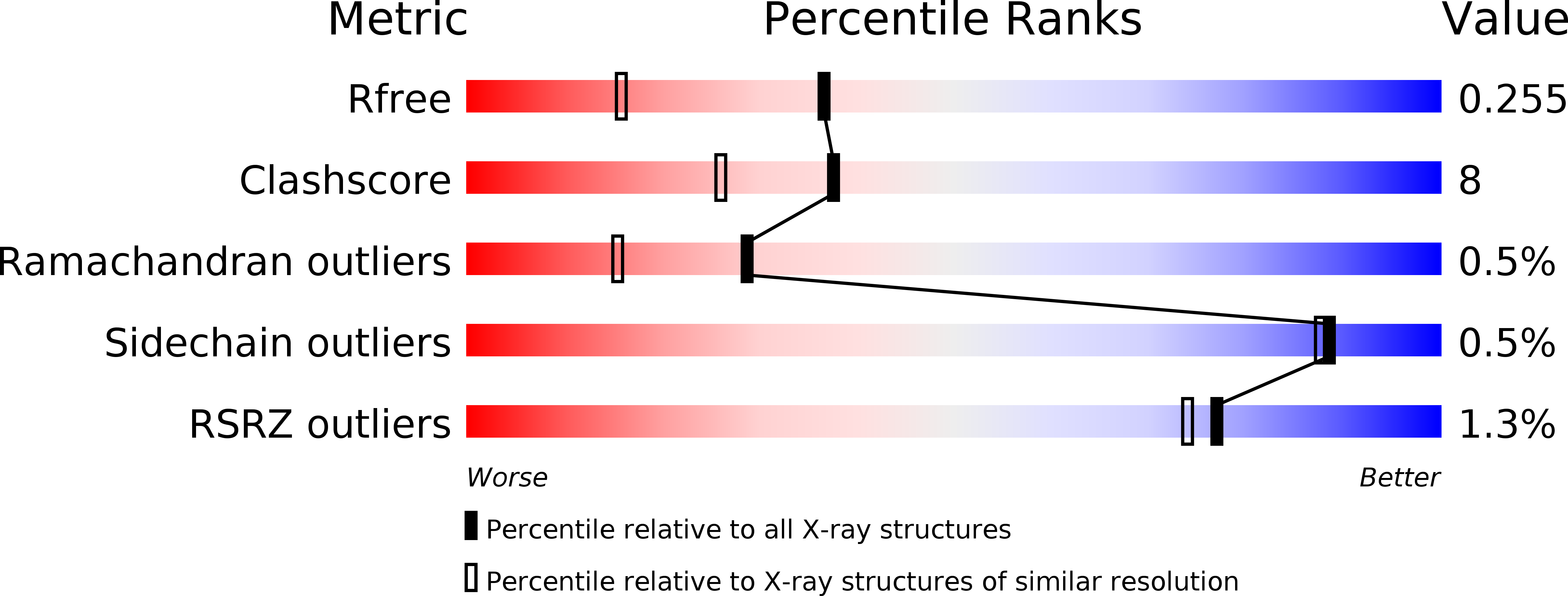
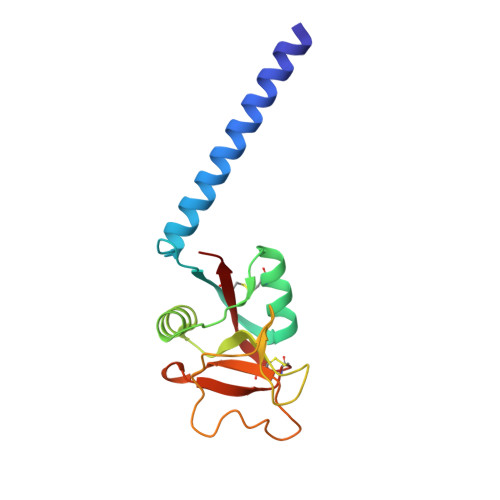
Trimeric structure of a C-type mannose-binding protein.
Weis, W.I., Drickamer, K.(1994) Structure 2: 1227-1240
- PubMed: 7704532
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-2126(94)00124-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1RTM - PubMed Abstract:
Mannose-binding proteins (MBPs) are C-type (Ca(2+)-dependent) animal lectins found in serum. They recognize cell-surface oligosaccharide structures characteristic of pathogenic bacteria and fungi, and trigger the neutralization of these organisms. Like most lectins, MBPs display weak intrinsic affinity for monovalent sugar ligands, but bind avidly to multivalent ligands. We report physical studies in solution and the crystal structure determined at 1.8 A Bragg spacings of a trimeric fragment of MBP-A, containing the carbohydrate-recognition domain (CRD) and the neck domain that links the carboxy-terminal CRD to the collagen-like portion of the intact molecule. The neck consists of a parallel triple-stranded coiled coil of alpha-helices linked by four residues to the CRD. The isolated neck peptide does not form stable helices in aqueous solution. The previously characterized carbohydrate-binding sites lie at the distal end of the trimer and are separated from each other by 53 A. The carbohydrate-binding sites in MBP-A are too far apart for a single trimer to bind multivalently to a typical mammalian high-mannose oligosaccharide. Thus MBPs can recognize pathogens selectively by binding avidly only to the widely spaced, repetitive sugar arrays on pathogenic cell surfaces. Sequence alignments reveal that other C-type lectins are likely to have a similar oligomeric structure, but differences in their detailed organization will have an important role in determining their interactions with oligosaccharides.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Structural Biology, Stanford University School of Medicine, CA 94305.