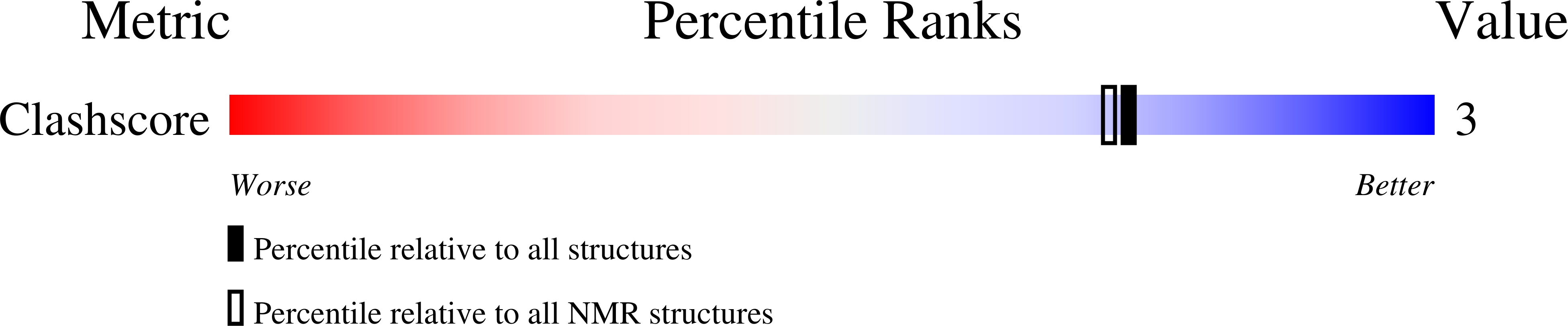NMR structure of the DNA decamer duplex containing double T*G mismatches of cis-syn cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer: implications for DNA damage recognition by the XPC-hHR23B complex.
Lee, J.H., Park, C.J., Shin, J.S., Ikegami, T., Akutsu, H., Choi, B.S.(2004) Nucleic Acids Res 32: 2474-2481
- PubMed: 15121904
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh568
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1PIB, 1SNH - PubMed Abstract:
The cis-syn cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer (CPD) is a cytotoxic, mutagenic and carcinogenic DNA photoproduct and is repaired by the nucleotide excision repair (NER) pathway in mammalian cells. The XPC-hHR23B complex as the initiator of global genomic NER binds to sites of certain kinds of DNA damage. Although CPDs are rarely recognized by the XPC-hHR23B complex, the presence of mismatched bases opposite a CPD significantly increased the binding affinity of the XPC-hHR23B complex to the CPD. In order to decipher the properties of the DNA structures that determine the binding affinity for XPC-hHR23B to DNA, we carried out structural analyses of the various types of CPDs by NMR spectroscopy. The DNA duplex which contains a single 3' T*G wobble pair in a CPD (CPD/GA duplex) induces little conformational distortion. However, severe distortion of the helical conformation occurs when a CPD contains double T*G wobble pairs (CPD/GG duplex) even though the T residues of the CPD form stable hydrogen bonds with the opposite G residues. The helical bending angle of the CPD/GG duplex was larger than those of the CPD/GA duplex and properly matched CPD/AA duplex. The fluctuation of the backbone conformation and significant changes in the widths of the major and minor grooves at the double T*G wobble paired site were also observed in the CPD/GG duplex. These structural features were also found in a duplex that contains the (6-4) adduct, which is efficiently recognized by the XPC-hHR23B complex. Thus, we suggest that the unique structural features of the DNA double helix (that is, helical bending, flexible backbone conformation, and significant changes of the major and/or minor grooves) might be important factors in determining the binding affinity of the XPC-hHR23B complex to DNA.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and National Creative Research Initiative Center, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, 373-1, Guseong-dong, Yuseong-gu, Daejon 305-701, Korea.