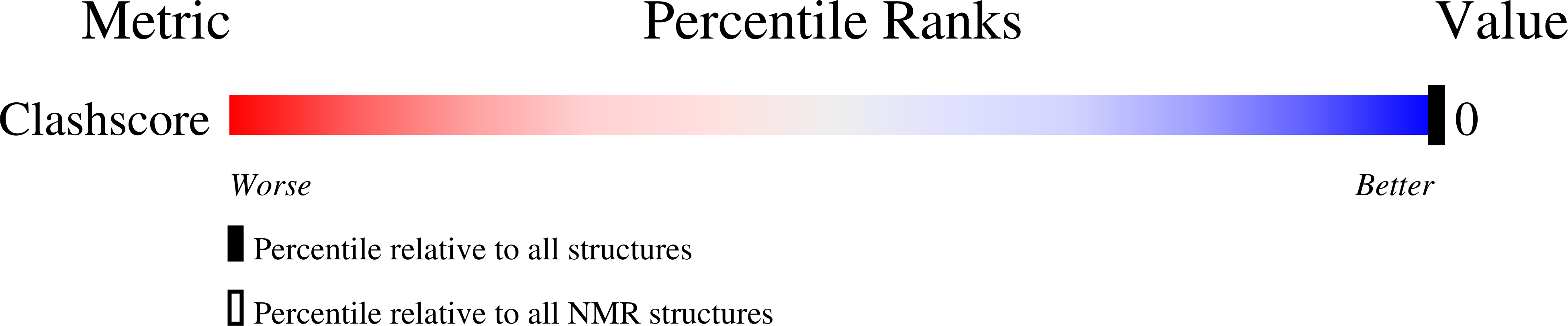A nicked duplex decamer DNA with a PEG(6) tether.
Kozerski, L., Mazurek, A.P., Kawecki, R., Bocian, W., Krajewski, P., Bednarek, E., Sitkowski, J., Williamson, M.P., Moir, A.J., Hansen, P.E.(2001) Nucleic Acids Res 29: 1132-1143
- PubMed: 11222763
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.5.1132
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1G1N - PubMed Abstract:
A dumbbell double-stranded DNA decamer tethered with a hexaethylene glycol linker moiety (DDSDPEG), with a nick in the centre of one strand, has been synthesised. The standard NMR methods, E.COSY, TOCSY, NOESY and HMQC, were used to measure (1)H, (31)P and T:(1) spectral parameters. Molecular modelling using rMD-simulated annealing was used to compute the structure. Scalar couplings and dipolar contacts show that the molecule adopts a right-handed B-DNA helix in 38 mM phosphate buffer at pH 7. Its high melting temperature confirms the good base stacking and stability of the duplex. This is partly attributed to the presence of the PEG(6) linker at both ends of the duplex that restricts the dynamics of the stem pentamers and thus stabilises the oligonucleotide. The inspection of the global parameters shows that the linker does not distort the B-DNA geometry. The computed structure suggests that the presence of the nick is not disturbing the overall tertiary structure, base pair geometry or duplex base pairing to a substantial extent. The nick has, however, a noticeable impact on the local geometry at the nick site, indicated clearly by NMR analysis and reflected in the conformational parameters of the computed structure. The (1)H spectra also show much sharper resonances in the presence of K(+) indicating that conformational heterogeneity of DDSDPEG is reduced in the presence of potassium as compared to sodium or caesium ions. At the same time the (1)H resonances have longer T:(1) times. This parameter is suggested as a sensitive gauge of stabilisation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Drug Institute, 00-725 Warszawa, Chetmska 30/34, Poland, Institute of Organic Chemistry, Polish Academy of Sciences, 01-224 Warszawa, Kasprzaka 44, Poland. lkoz@ichf.edu.pl