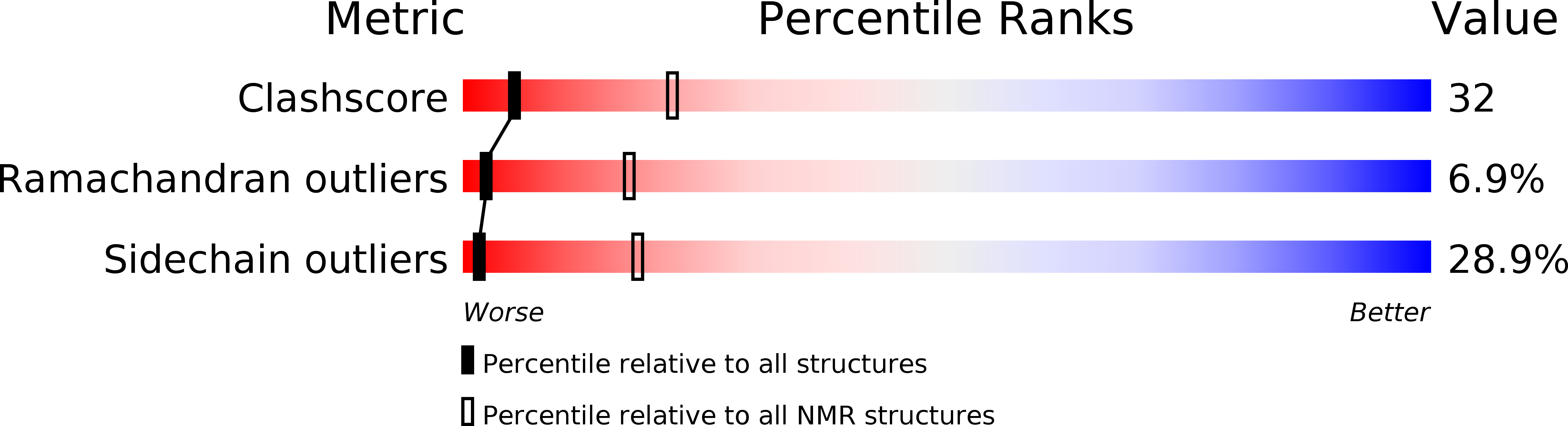Structure of a soluble, glycosylated form of the human complement regulatory protein CD59.
Fletcher, C.M., Harrison, R.A., Lachmann, P.J., Neuhaus, D.(1994) Structure 2: 185-199
- PubMed: 7520819
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00020-4
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1CDQ, 1CDR, 1CDS - PubMed Abstract:
CD59 is a cell-surface glycoprotein that protects host cells from complement-mediated lysis by binding to and preventing the normal functioning of the complement proteins C8 and/or C9 which form part of a membrane penetrating assembly called the membrane attack complex. CD59 has no structural similarity to other complement proteins, but is an example of a plasma protein domain type found also in murine Ly-6 proteins and the urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor. CD59 was purified from human urine, retaining the N-glycan and at least some of the non-lipid component of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane anchor. The three-dimensional structure of the protein component has been determined in the presence of the carbohydrate groups using two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. The protein structure is well defined by the NMR data (root mean square deviation from the mean structure of 0.65 A for backbone atoms and no distance constraint violations greater than 0.4 A). Structure calculations were also carried out to model the orientation of the N-acetylglucosamine residue that is directly linked to Asn18. The main features of the protein structure are two antiparallel beta-sheets (a central one with three strands and another with two), a short helix that packs against the three-stranded beta-sheet, and a carboxy-terminal region that, although lacking regular secondary structure, is well defined and packs against the three-stranded beta-sheet, on the opposite face to the helix. We have used the structure, in combination with existing biochemical data, to identify residues that may be involved in C8 binding.
Organizational Affiliation:
MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Cambridge, UK.