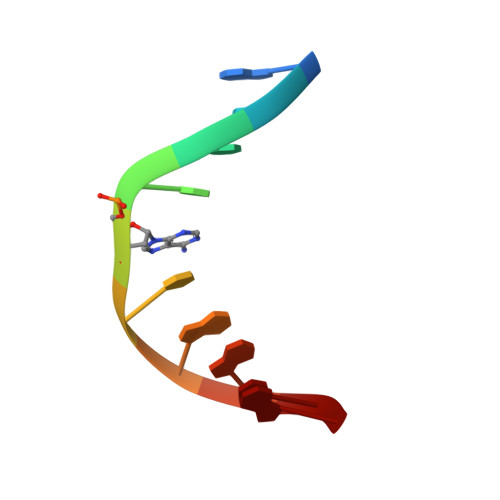
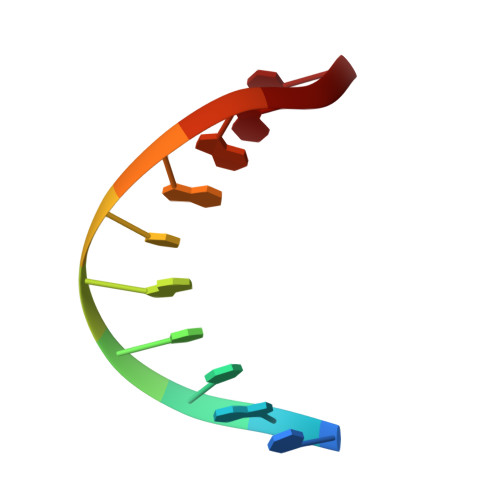
Solution Structure of a DNA Duplex Containing an alpha-Anomeric Adenosine: Insights into Substrate Recognition by Endonuclease IV.
Aramini, J.M., Cleaver, S.H., Pon, R.T., Cunningham, R.P., Germann, M.W.(2004) J Mol Biol 338: 77-91
- PubMed: 15050824
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.02.035
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1S0T, 1S74, 1S75 - PubMed Abstract:
The cytotoxic alpha anomer of adenosine, generated in situ by radicals, must be recognized and repaired to maintain genomic stability. Endonuclease IV (Endo IV), a member of the base excision repair (BER) enzyme family, in addition to acting on abasic sites, has the auxiliary function of removing this mutagenic nucleotide in Escherichia coli. We have employed enzymatic, thermodynamic, and structural studies on DNA duplexes containing a central alpha-anomeric adenosine residue to characterize the role of DNA structure on recognition and catalysis by Endo IV. The enzyme recognizes and cleaves our alphaA-containing DNA duplexes at the site of the modification. The NMR solution structure of the DNA decamer duplex establishes that the single alpha-anomeric adenosine residue is intrahelical and stacks in a reverse Watson-Crick fashion consistent with the slight decrease in thermostability. However, the presence of this lesion confers significant changes to the global duplex conformation, resulting from a kink of the helical axis into the major groove and an opening of the minor groove emanating from the alpha-anomeric site. Interestingly, the conformation of the flanking base-paired segments is not greatly altered from a B-type conformation. The global structural changes caused by this lesion place the DNA along the conformational path leading to the DNA structure observed in the complex. Thus, it appears that the alpha-anomeric lesion facilitates recognition by Endo IV.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Georgia State University, Atlanta, GA 30303, USA.