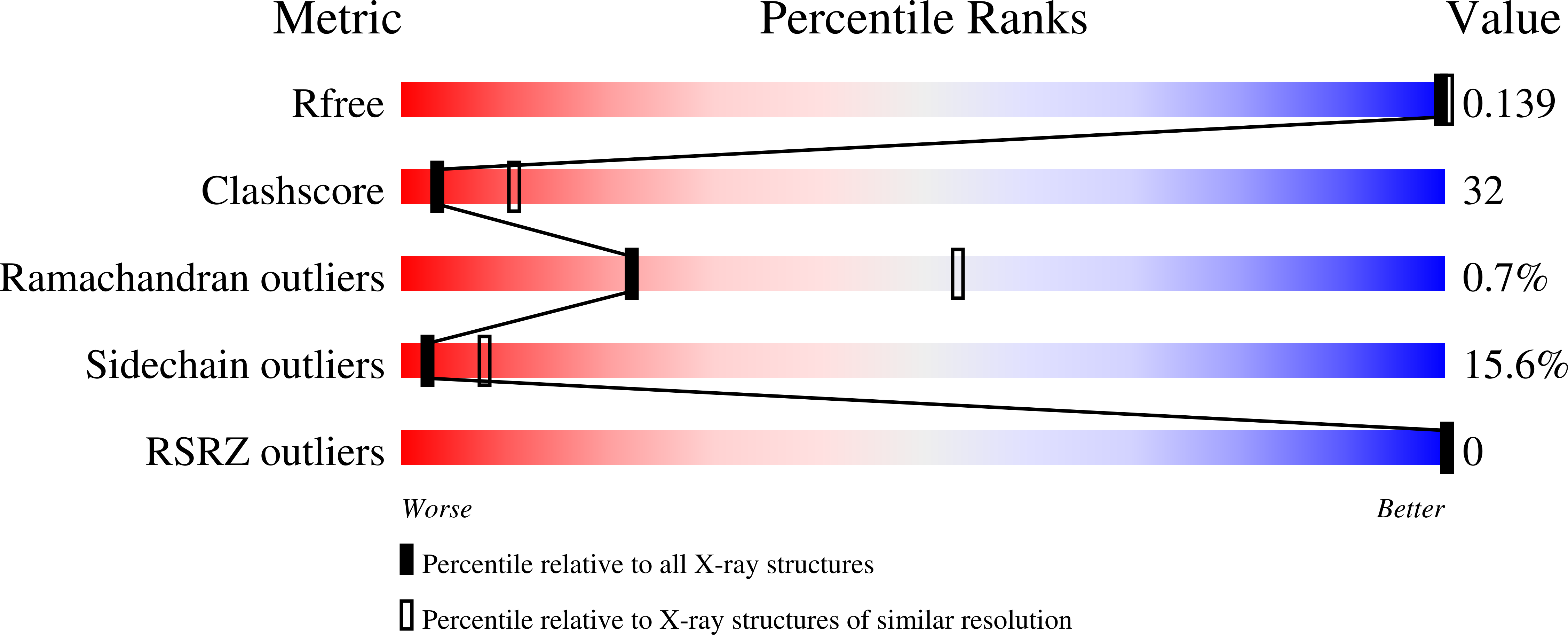
X-ray crystallographic analyses of inhibitor and substrate complexes of wild-type and mutant 4-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA thioesterase.
Thoden, J.B., Holden, H.M., Zhuang, Z., Dunaway-Mariano, D.(2002) J Biol Chem 277: 27468-27476
- PubMed: 11997398
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M203904200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1LO7, 1LO8, 1LO9 - PubMed Abstract:
The metabolic pathway by which 4-chlorobenzoate is degraded to 4-hydroxybenzoate in the soil-dwelling microbe Pseudomonas sp. strain CBS-3 consists of three enzymes including 4-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA thioesterase. The structure of the unbound form of this thioesterase has been shown to contain the so-called "hot dog" fold with a large helix packed against a five-stranded anti-parallel beta-sheet. To address the manner in which the enzyme accommodates the substrate within the active site, two inhibitors have been synthesized, namely 4-hydroxyphenacyl-CoA and 4-hydroxybenzyl-CoA. Here we describe the structural analyses of the enzyme complexed with these two inhibitors determined and refined to 1.5 and 1.8 A resolution, respectively. These studies indicate that only one protein side chain, Ser(91), participates directly in ligand binding. All of the other interactions between the protein and the inhibitors are mediated through backbone peptidic NH groups, carbonyl oxygens, and/or solvents. The structures of the enzyme-inhibitor complexes suggest that both a hydrogen bond and the positive end of a helix dipole moment serve to polarize the electrons away from the carbonyl carbon of the acyl group, thereby making it more susceptible to nucleophilic attack. Additionally, these studies demonstrate that the carboxylate group of Asp(17) is approximately 3.2 A from the carbonyl carbon of the acyl group. To address the role of Asp(17), the structure of the site-directed mutant protein D17N with bound substrate has also been determined. Taken together, these investigations suggest that the reaction mechanism may proceed through an acyl enzyme intermediate.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Wisconsin, 433 Babcock Drive, Madison, WI 53706-1544, USA.