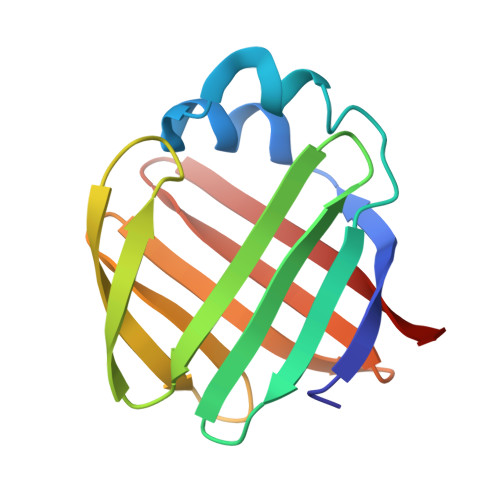
Solution structure of ileal lipid binding protein in complex with glycocholate.
Luecke, C., Zhang, F., Hamilton, J.A., Sacchettini, J.C., Rueterjans, H.(2000) Eur J Biochem 267: 2929-2938
- PubMed: 10806391
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01307.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1EIO - PubMed Abstract:
Ileal lipid binding protein (ILBP) is a cytosolic lipid-binding protein that binds both bile acids and fatty acids. We have determined the solution structure of porcine ILBP in complex with glycocholate by homonuclear and heteronuclear two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. The conformation of the protein-ligand complex was determined by restrained energy minimization and simulated annealing calculations after docking the glycocholate ligand into the protein structure. The overall tertiary structure of ILBP is highly analogous to the three-dimensional structures of several other intracellular lipid binding proteins (LBPs). Like the apo-structure, the bile-acid complex of ILBP is composed of 10 anti-parallel beta-strands that form a water-filled clam-shell structure, and two short alpha-helices. Chemical shift data indicated that the bile acid ligand is bound inside the protein cavity. Furthermore, 13C-edited heteronuclear single-quantum correlation-NOESY experiments showed NOE contacts between several aromatic residues located in the proposed bile acid portal region and the 13C-labeled ligand. A single bile acid molecule is bound inside the protein, with the steroid moiety penetrating deep into the water-accessible internal cavity, such that ring A is located right above the plane of the Trp49 indole ring. The carboxylate tail of the ligand is protruding from the proposed bile acid portal into the surrounding aqueous solution. The body of the steroid moiety is oriented with the nonpolar face in contact with the mostly hydrophobic residues of beta-strands C, D and E, while the polar face shows contacts with the side-chains of Tyr97, His99, Glu110 and Arg121 in beta-strands H, I and J. Thus, the conformational arrangement of the ligand complex suggests that the binding affinity of ILBP for bile acid molecules is based mainly on strong hydrophobic interactions inside the protein cavity. Furthermore, this binding mode explains how ILBP can transport unconjugated and conjugated bile acids.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institut für Biophysikalische Chemie, J. W. Goethe-Universität, Frankfurt a.M., Germany.