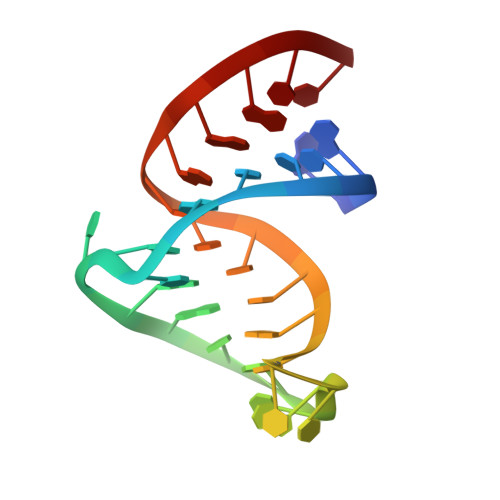
Molecular recognition in the bovine immunodeficiency virus Tat peptide-TAR RNA complex.
Ye, X., Kumar, R.A., Patel, D.J.(1995) Chem Biol 2: 827-840
- PubMed: 8807816
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/1074-5521(95)90089-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1BIV - PubMed Abstract:
In lentiviruses such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and bovine immunodeficiency virus (BIV), the Tat (trans-activating) protein enhances transcription of the viral RNA by complexing to the 5'-end of the transcribed mRNA, at a region known as TAR (the trans-activation response element). Identification of the determinants that account for specific molecular recognition requires a high resolution structure of the Tat peptide-TAR RNA complex. We report here on the structural characterization of a complex of the recognition domains of BIV Tat and TAR in aqueous solution using a combination of NMR and molecular dynamics. The 17-mer Tat peptide recognition domain folds into a beta-hairpin and penetrates in an edge-on orientation deep into a widened major groove of the 28-mer TAR RNA recognition domain in the complex. The RNA fold is defined, in part, by two uracil bulged bases; U12 has a looped-out conformation that widens the major groove and U10 forms a U.AU base triple that buttresses the RNA helix. Together, these bulged bases induce a approximately 40 degree bend between the two helical stems of the TAR RNA in the complex. A set of specific intermolecular hydrogen bonds between arginine side chains and the major-groove edge of guanine residues contributes to sequence specificity. These peptide-RNA contacts are complemented by other intermolecular hydrogen bonds and intermolecular hydrophobic packing contacts involving glycine and isoleucine side chains. We have identified a new structural motif for protein-RNA recognition, a beta-hairpin peptide that interacts with the RNA major groove. Specificity is associated with formation of a novel RNA structural motif, a U.AU base triple, which facilitates hydrogen bonding of an arginine residue to a guanine and to a backbone phosphate. These results should facilitate the design of inhibitors that can disrupt HIV Tat-TAR association.
Organizational Affiliation:
Cellular Biochemistry & Biophysics Program, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY 10021, USA.