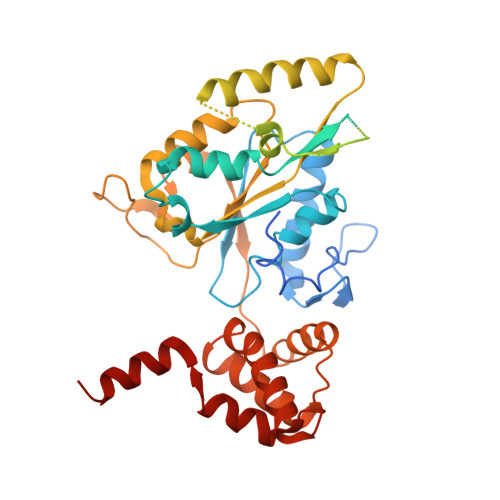
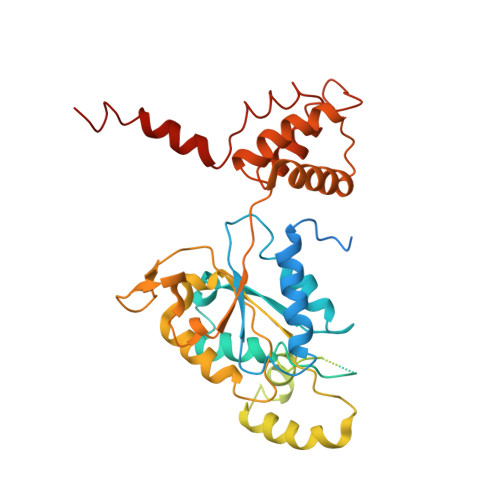
Regulation of RUVBL1-RUVBL2 AAA-ATPases by the nonsense-mediated mRNA decay factor DHX34, as evidenced by Cryo-EM.
Lopez-Perrote, A., Hug, N., Gonzalez-Corpas, A., Rodriguez, C.F., Serna, M., Garcia-Martin, C., Boskovic, J., Fernandez-Leiro, R., Caceres, J.F., Llorca, O.(2020) Elife 9
- PubMed: 33205750
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.63042
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7AHO - PubMed Abstract:
Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) is a surveillance pathway that degrades aberrant mRNAs and also regulates the expression of a wide range of physiological transcripts. RUVBL1 and RUVBL2 AAA-ATPases form an hetero-hexameric ring that is part of several macromolecular complexes such as INO80, SWR1, and R2TP. Interestingly, RUVBL1-RUVBL2 ATPase activity is required for NMD activation by an unknown mechanism. Here, we show that DHX34, an RNA helicase regulating NMD initiation, directly interacts with RUVBL1-RUVBL2 in vitro and in cells. Cryo-EM reveals that DHX34 induces extensive changes in the N-termini of every RUVBL2 subunit in the complex, stabilizing a conformation that does not bind nucleotide and thereby down-regulates ATP hydrolysis of the complex. Using ATPase-deficient mutants, we find that DHX34 acts exclusively on the RUVBL2 subunits. We propose a model, where DHX34 acts to couple RUVBL1-RUVBL2 ATPase activity to the assembly of factors required to initiate the NMD response.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biology Programme, Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), Madrid, Spain.