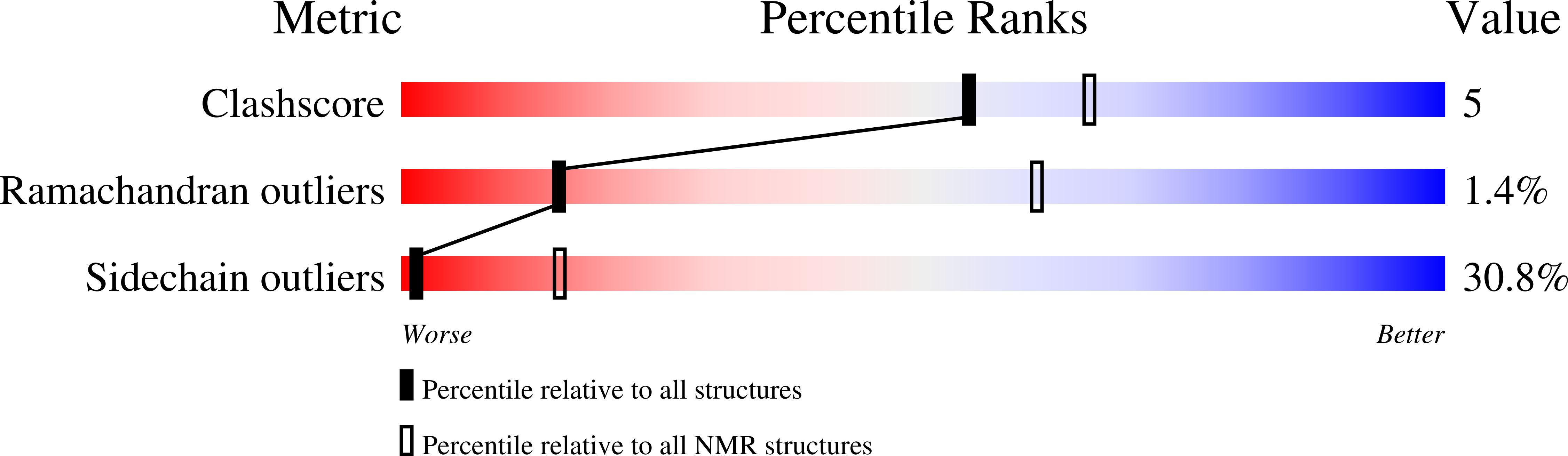Small-molecule antagonism of the interaction of the RAGE cytoplasmic domain with DIAPH1 reduces diabetic complications in mice.
Manigrasso, M.B., Rabbani, P., Egana-Gorrono, L., Quadri, N., Frye, L., Zhou, B., Reverdatto, S., Ramirez, L.S., Dansereau, S., Pan, J., Li, H., D'Agati, V.D., Ramasamy, R., DeVita, R.J., Shekhtman, A., Schmidt, A.M.(2021) Sci Transl Med 13: eabf7084-eabf7084
- PubMed: 34818060
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.abf7084
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6VXG - PubMed Abstract:
The macro- and microvascular complications of type 1 and 2 diabetes lead to increased disease severity and mortality. The receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) can bind AGEs and multiple proinflammatory ligands that accumulate in diabetic tissues. Preclinical studies indicate that RAGE antagonists have beneficial effects on numerous complications of diabetes. However, these antagonists target the extracellular domains of RAGE, which bind distinct RAGE ligands at diverse sites in the immunoglobulin-like variable domain and two constant domains. The cytoplasmic tail of RAGE (ctRAGE) binds to the formin, Diaphanous-1 (DIAPH1), and this interaction is important for RAGE signaling. To comprehensively capture the breadth of RAGE signaling, we developed small-molecule antagonists of ctRAGE-DIAPH1 interaction, termed RAGE229. We demonstrated that RAGE229 is effective in suppressing RAGE-DIAPH1 binding, Förster resonance energy transfer, and biological activities in cellular assays. Using solution nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, we defined the molecular underpinnings of the interaction of RAGE229 with RAGE. Through in vivo experimentation, we showed that RAGE229 assuaged short- and long-term complications of diabetes in both male and female mice, without lowering blood glucose concentrations. Last, the treatment with RAGE229 reduced plasma concentrations of TNF-α, IL-6, and CCL2/JE-MCP1 in diabetic mice, in parallel with reduced pathological and functional indices of diabetes-like kidney disease. Targeting ctRAGE-DIAPH1 interaction with RAGE229 mitigated diabetic complications in rodents by attenuating inflammatory signaling.
Organizational Affiliation:
Diabetes Research Program, Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism, NYU Langone Health, New York, NY 10016, USA.