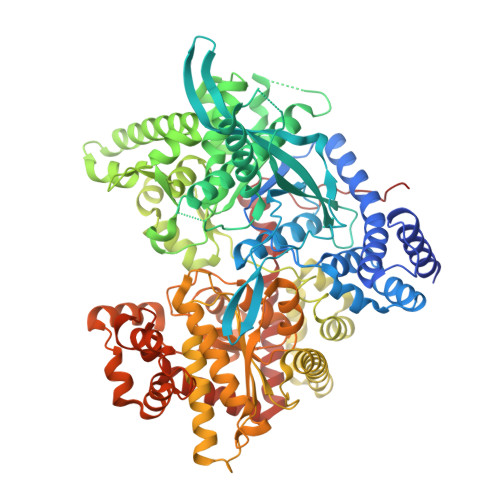
Insights into Brain Glycogen Metabolism: THE STRUCTURE OF HUMAN BRAIN GLYCOGEN PHOSPHORYLASE.
Mathieu, C., de la Sierra-Gallay, I.L., Duval, R., Xu, X., Cocaign, A., Leger, T., Woffendin, G., Camadro, J.M., Etchebest, C., Haouz, A., Dupret, J.M., Rodrigues-Lima, F.(2016) J Biol Chem 291: 18072-18083
- PubMed: 27402852
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.738898
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5IKO, 5IKP - PubMed Abstract:
Brain glycogen metabolism plays a critical role in major brain functions such as learning or memory consolidation. However, alteration of glycogen metabolism and glycogen accumulation in the brain contributes to neurodegeneration as observed in Lafora disease. Glycogen phosphorylase (GP), a key enzyme in glycogen metabolism, catalyzes the rate-limiting step of glycogen mobilization. Moreover, the allosteric regulation of the three GP isozymes (muscle, liver, and brain) by metabolites and phosphorylation, in response to hormonal signaling, fine-tunes glycogenolysis to fulfill energetic and metabolic requirements. Whereas the structures of muscle and liver GPs have been known for decades, the structure of brain GP (bGP) has remained elusive despite its critical role in brain glycogen metabolism. Here, we report the crystal structure of human bGP in complex with PEG 400 (2.5 Å) and in complex with its allosteric activator AMP (3.4 Å). These structures demonstrate that bGP has a closer structural relationship with muscle GP, which is also activated by AMP, contrary to liver GP, which is not. Importantly, despite the structural similarities between human bGP and the two other mammalian isozymes, the bGP structures reveal molecular features unique to the brain isozyme that provide a deeper understanding of the differences in the activation properties of these allosteric enzymes by the allosteric effector AMP. Overall, our study further supports that the distinct structural and regulatory properties of GP isozymes contribute to the different functions of muscle, liver, and brain glycogen.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Université Paris Diderot, Sorbonne Paris Cité, Unité BFA, CNRS UMR 8251, 75013 Paris, France.