The Structure and Biochemical Properties of the Human Spliceosomal Protein U1C
Muto, Y., Pomeranz-Krummel, D., Oubridge, C., Hernandez, H., Robinson, C., Neuhaus, D., Nagai, K.(2004) J Mol Biol 341: 185
- PubMed: 15312772
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.04.078
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2VRD - PubMed Abstract:
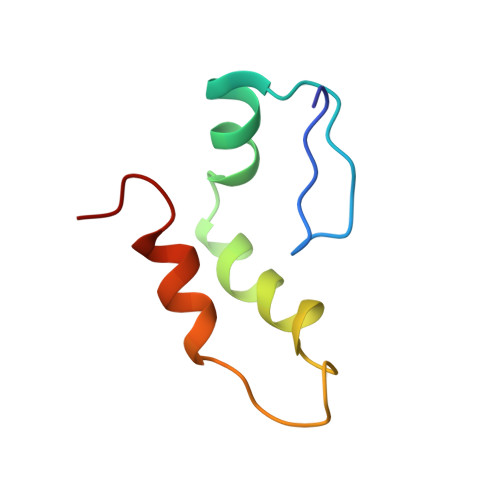
The spliceosomal U1C protein is critical to the initiation and regulation of precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) splicing, as part of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle (snRNP). We have produced full-length and 61 residue constructs of human U1C in soluble form in Escherichia coli. Atomic absorption spectroscopy and mass spectrometry show that both constructs contain one Zn atom and are monomeric. Gelmobility-shift assays showed that one molecule of recombinant U1C, either full-length or 61 residue construct, can be incorporated into the U1 snRNP core domain in the presence of U1 70k. This result is in perfect agreement with the previous experiment with U1C isolated from the HeLa U1 snRNP showing that the recombinant U1C is functionally active. We have determined the solution structure of the N-terminal 61 residue construct of U1C by NMR. A Cys(2)His(2)-type zinc finger, distinct from the TFIIIA-type, is extended at its C terminus by two additional helices. The two Zn-coordinating histidine residues are separated by a five residue loop. The conserved basic residues in the first two helices and the intervening loop may be involved in RNA binding. The opposite beta-sheet face with two surface-exposed Tyr residues may be involved in protein contacts. Both the full-length and 61 residue constructs of human U1C fail to bind RNA containing the 5' splice site sequence, in contrast to what has been reported for the Saccharomyces cerevisiae orthologue.
Organizational Affiliation:
MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 2QH, UK.