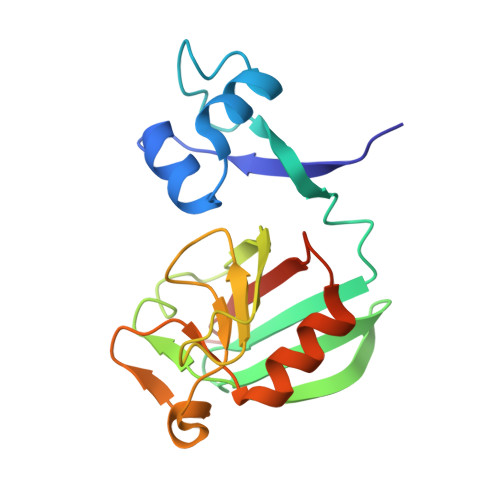
Atomic model of a cell-wall cross-linking enzyme in complex with an intact bacterial peptidoglycan.
Schanda, P., Triboulet, S., Laguri, C., Bougault, C.M., Ayala, I., Callon, M., Arthur, M., Simorre, J.P.(2014) J Am Chem Soc 136: 17852-17860
- PubMed: 25429710
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja5105987
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2MTZ - PubMed Abstract:
The maintenance of bacterial cell shape and integrity is largely attributed to peptidoglycan, a highly cross-linked biopolymer. The transpeptidases that perform this cross-linking are important targets for antibiotics. Despite this biomedical importance, to date no structure of a protein in complex with an intact bacterial peptidoglycan has been resolved, primarily due to the large size and flexibility of peptidoglycan sacculi. Here we use solid-state NMR spectroscopy to derive for the first time an atomic model of an l,d-transpeptidase from Bacillus subtilis bound to its natural substrate, the intact B. subtilis peptidoglycan. Importantly, the model obtained from protein chemical shift perturbation data shows that both domains-the catalytic domain as well as the proposed peptidoglycan recognition domain-are important for the interaction and reveals a novel binding motif that involves residues outside of the classical enzymatic pocket. Experiments on mutants and truncated protein constructs independently confirm the binding site and the implication of both domains. Through measurements of dipolar-coupling derived order parameters of bond motion we show that protein binding reduces the flexibility of peptidoglycan. This first report of an atomic model of a protein-peptidoglycan complex paves the way for the design of new antibiotic drugs targeting l,d-transpeptidases. The strategy developed here can be extended to the study of a large variety of enzymes involved in peptidoglycan morphogenesis.
Organizational Affiliation:
University Grenoble Alpes, IBS , F-38044 Grenoble, France.