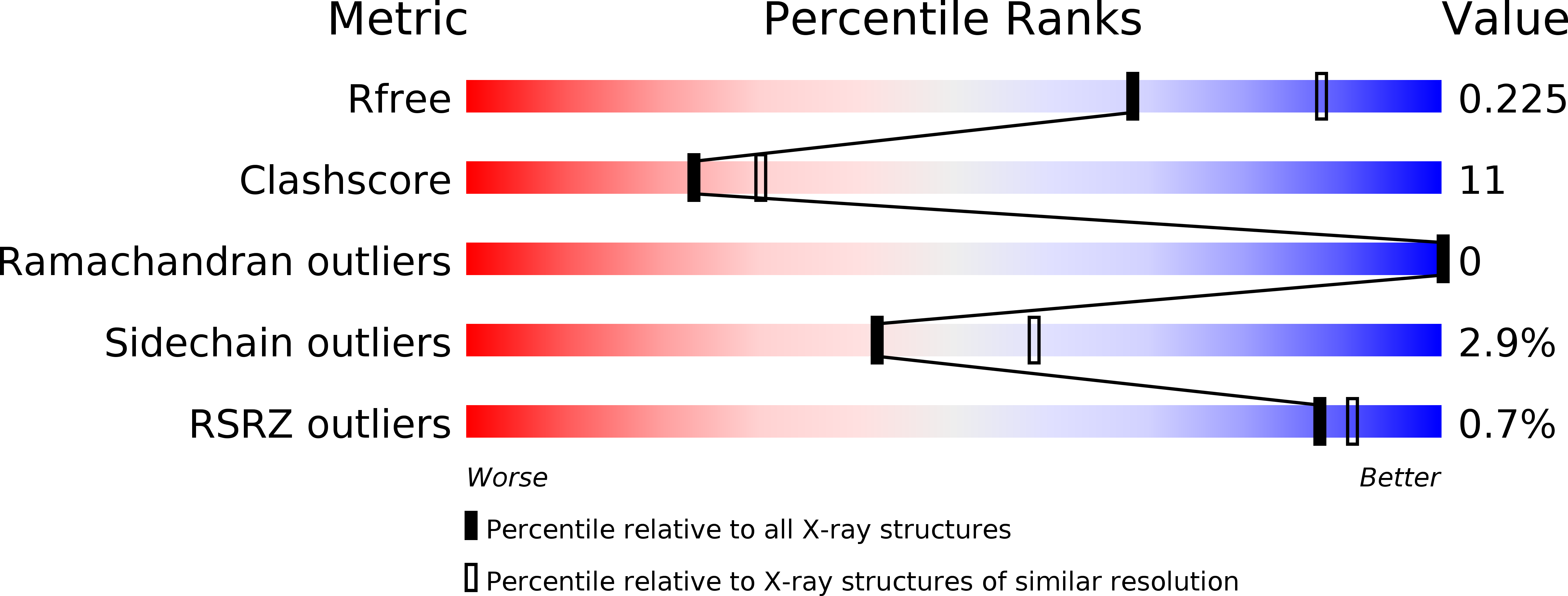
Crystal structure of an invertebrate caspase.
Forsyth, C.M., Lemongello, D., LaCount, D.J., Friesen, P.D., Fisher, A.J.(2004) J Biol Chem 279: 7001-7008
- PubMed: 14645217
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M312472200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1M72 - PubMed Abstract:
Caspases play an essential role in the execution of apoptosis. These cysteine proteases are highly conserved among metazoans and are translated as inactive zymogens, which are activated by proteolytic cleavages to generate the large and small subunits and remove the N-terminal prodomain. The 2.3 A resolution crystal structure of active Sf-caspase-1, the principal effector caspase of the insect Spodoptera frugiperda, is presented here. The structure represents the first nonhuman caspase to be resolved. The structure of the cleaved and active protease was determined with the tetrapeptide inhibitor N-acetyl-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-chloromethylketone covalently bonded to the active site cysteine. As expected, the overall fold of Sf-caspase-1 is exceedingly similar to that of the five active caspases from humans solved to date. The overall structure and active site arrangement of Sf-caspase-1 is most comparable with that of the human effector caspases, with which it shares highest sequence homology. The most prominent structural difference with Sf-caspase-1 is the position of the N-terminal region of the large subunit. Unlike the N terminus of human caspases, the N terminus of Sf-caspase-1 originates from the active site side where it interacts with active site loop L2 and then extends to the backside of the heterodimer. This unusual structural arrangement raises the possibility that the N-terminal prodomain plays a regulatory role during effector caspase activation or enzyme activity in insects.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Section of Molecular and Cellular Biology, University of California, Davis 95616, USA.