Identification and characterization of endo-alpha-, exo-alpha-, and exo-beta-D-arabinofuranosidases degrading lipoarabinomannan and arabinogalactan of mycobacteria.
Shimokawa, M., Ishiwata, A., Kashima, T., Nakashima, C., Li, J., Fukushima, R., Sawai, N., Nakamori, M., Tanaka, Y., Kudo, A., Morikami, S., Iwanaga, N., Akai, G., Shimizu, N., Arakawa, T., Yamada, C., Kitahara, K., Tanaka, K., Ito, Y., Fushinobu, S., Fujita, K.(2023) Nat Commun 14: 5803-5803
- PubMed: 37726269
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-41431-2
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
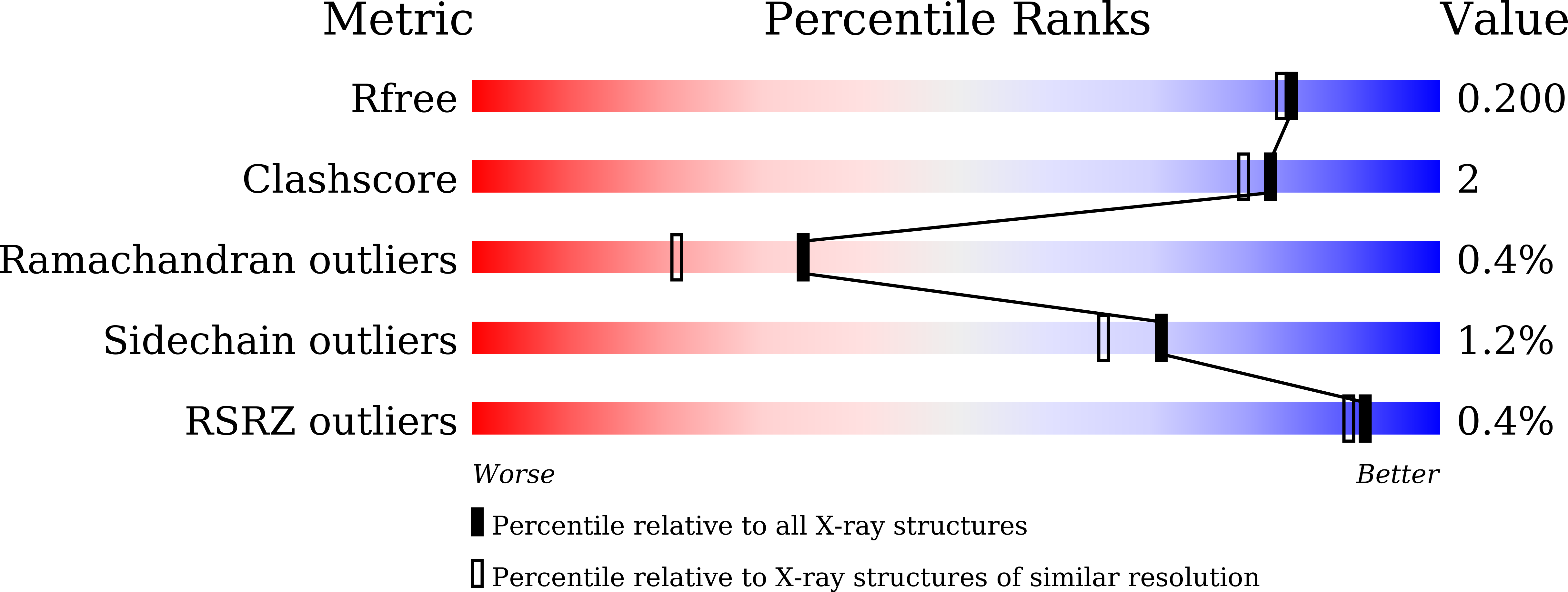
8HHV, 8IC1, 8IC6, 8IC7, 8IC8 - PubMed Abstract:
The cell walls of pathogenic and acidophilic bacteria, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium leprae, contain lipoarabinomannan and arabinogalactan. These components are composed of D-arabinose, the enantiomer of the typical L-arabinose found in plants. The unique glycan structures of mycobacteria contribute to their ability to evade mammalian immune responses. In this study, we identified four enzymes (two GH183 endo-D-arabinanases, GH172 exo-α-D-arabinofuranosidase, and GH116 exo-β-D-arabinofuranosidase) from Microbacterium arabinogalactanolyticum. These enzymes completely degraded the complex D-arabinan core structure of lipoarabinomannan and arabinogalactan in a concerted manner. Furthermore, through biochemical characterization using synthetic substrates and X-ray crystallography, we elucidated the mechanisms of substrate recognition and anomer-retaining hydrolysis for the α- and β-D-arabinofuranosidic bonds in both endo- and exo-mode reactions. The discovery of these D-arabinan-degrading enzymes, along with the understanding of their structural basis for substrate specificity, provides valuable resources for investigating the intricate glycan architecture of mycobacterial cell wall polysaccharides and their contribution to pathogenicity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Faculty of Agriculture, Kagoshima University, Kagoshima, 890-0065, Japan.