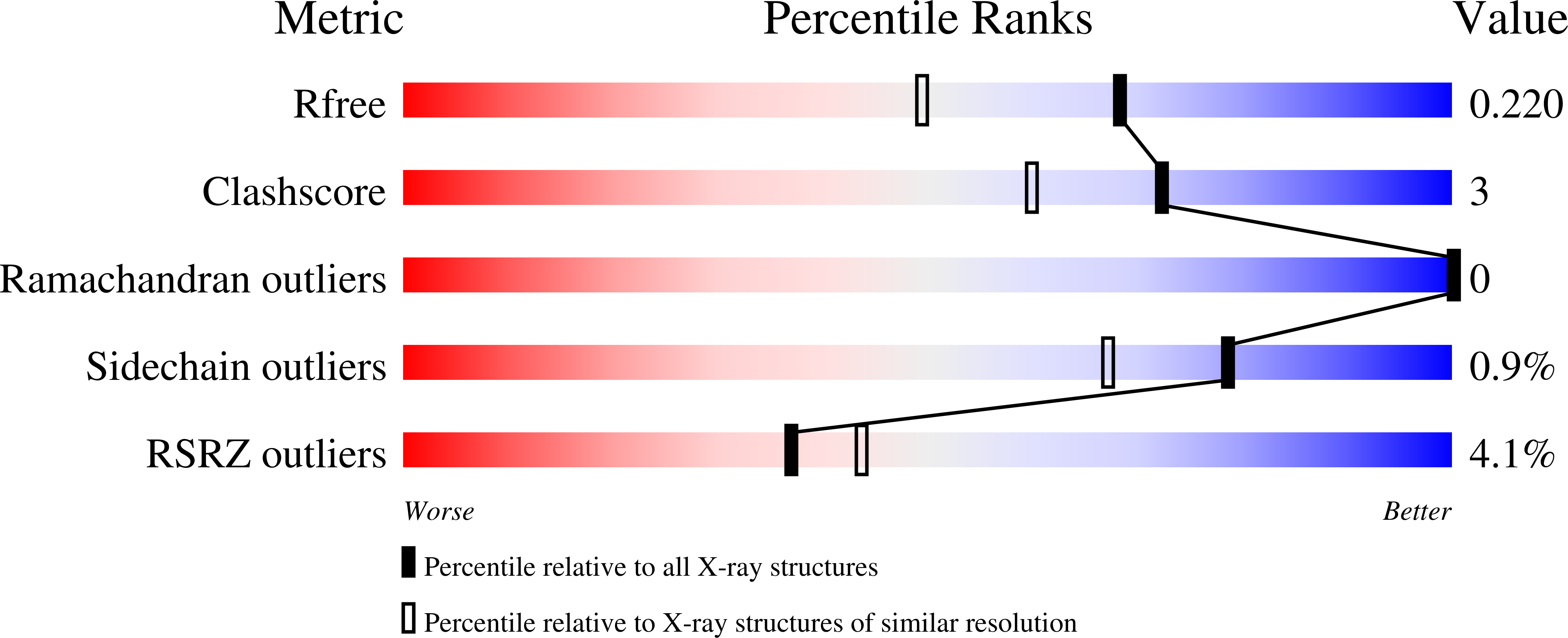
Thermococcus kodakarensis TK0353 is a novel AP lyase with a new fold.
Caffrey, P.J., Eckenroth, B.E., Burkhart, B.W., Zatopek, K.M., McClung, C.M., Santangelo, T.J., Doublie, S., Gardner, A.F.(2023) J Biol Chem 300: 105503-105503
- PubMed: 38013090
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105503
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8GM6, 8GM7, 8SYJ - PubMed Abstract:
Hyperthermophilic organisms thrive in extreme environments prone to high levels of DNA damage. Growth at high temperature stimulates DNA base hydrolysis resulting in apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) sites that destabilize the genome. Organisms across all domains have evolved enzymes to recognize and repair AP sites to maintain genome stability. The hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis encodes several enzymes to repair AP site damage including the essential AP endonuclease TK endonuclease IV. Recently, using functional genomic screening, we discovered a new family of AP lyases typified by TK0353. Here, using biochemistry, structural analysis, and genetic deletion, we have characterized the TK0353 structure and function. TK0353 lacks glycosylase activity on a variety of damaged bases and is therefore either a monofunctional AP lyase or may be a glycosylase-lyase on a yet unidentified substrate. The crystal structure of TK0353 revealed a novel fold, which does not resemble other known DNA repair enzymes. The TK0353 gene is not essential for T. kodakarensis viability presumably because of redundant base excision repair enzymes involved in AP site processing. In summary, TK0353 is a novel AP lyase unique to hyperthermophiles that provides redundant repair activity necessary for genome maintenance.
Organizational Affiliation:
New England Biolabs, Inc Ipswich, Massachusetts, USA.