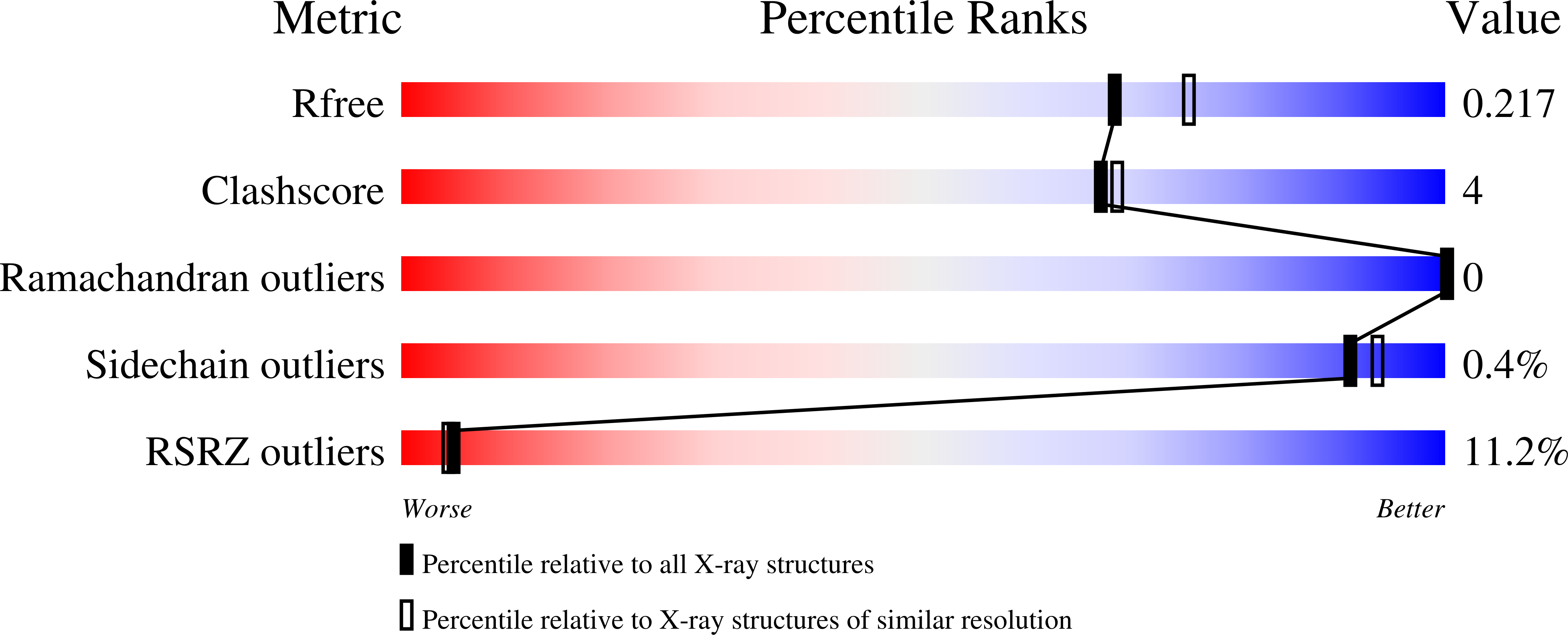
ClpP1P2 peptidase activity promotes biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Mawla, G.D., Hall, B.M., Carcamo-Oyarce, G., Grant, R.A., Zhang, J.J., Kardon, J.R., Ribbeck, K., Sauer, R.T., Baker, T.A.(2021) Mol Microbiol 115: 1094-1109
- PubMed: 33231899
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.14649
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7M1L, 7M1M - PubMed Abstract:
Caseinolytic proteases (Clp) are central to bacterial proteolysis and control cellular physiology and stress responses. They are composed of a double-ring compartmentalized peptidase (ClpP) and a AAA+ unfoldase (ClpX or ClpA/ClpC). Unlike many bacteria, the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa contains two ClpP homologs: ClpP1 and ClpP2. The specific functions of these homologs, however, are largely elusive. Here, we report that the active form of PaClpP2 is a part of a heteromeric PaClpP1 7 P2 7 tetradecamer that is required for proper biofilm development. PaClpP1 14 and PaClpP1 7 P2 7 complexes exhibit distinct peptide cleavage specificities and interact differentially with P. aeruginosa ClpX and ClpA. Crystal structures reveal that PaClpP2 has non-canonical features in its N- and C-terminal regions that explain its poor interaction with unfoldases. However, experiments in vivo indicate that the PaClpP2 peptidase active site uniquely contributes to biofilm development. These data strongly suggest that the specificity of different classes of ClpP peptidase subunits contributes to the biological outcome of proteolysis. This specialized role of PaClpP2 highlights it as an attractive target for developing antimicrobial agents that interfere specifically with late-stage P. aeruginosa development.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biology, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA.