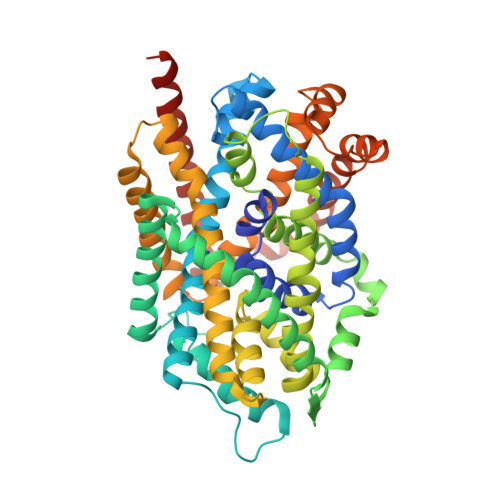
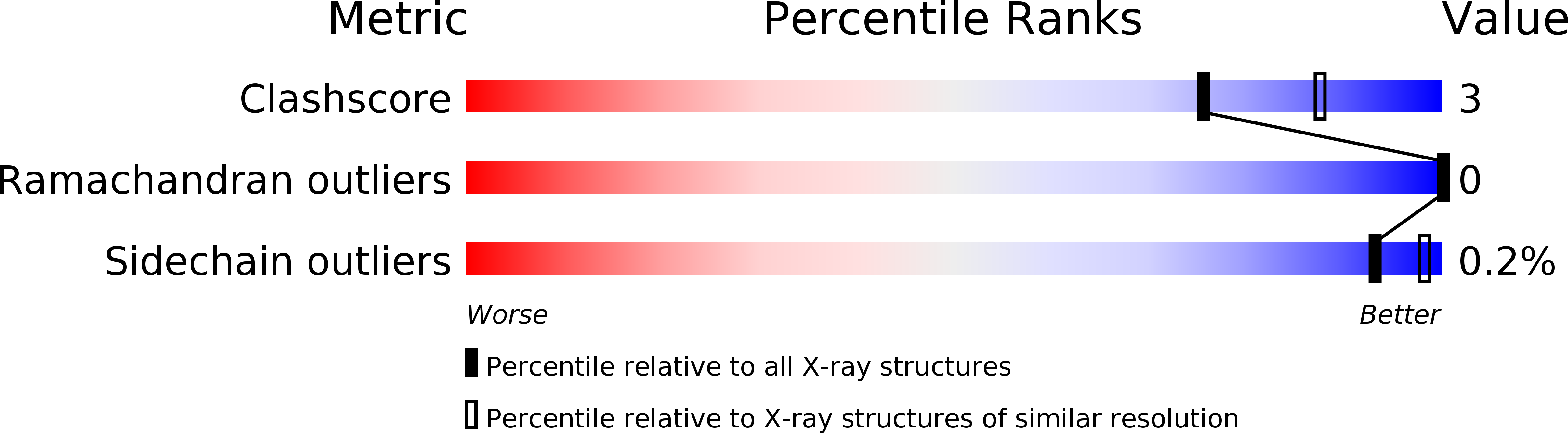X-ray structure of LeuT in an inward-facing occluded conformation reveals mechanism of substrate release.
Gotfryd, K., Boesen, T., Mortensen, J.S., Khelashvili, G., Quick, M., Terry, D.S., Missel, J.W., LeVine, M.V., Gourdon, P., Blanchard, S.C., Javitch, J.A., Weinstein, H., Loland, C.J., Nissen, P., Gether, U.(2020) Nat Commun 11: 1005-1005
- PubMed: 32081981
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14735-w
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6XWM - PubMed Abstract:
Neurotransmitter:sodium symporters (NSS) are conserved from bacteria to man and serve as targets for drugs, including antidepressants and psychostimulants. Here we report the X-ray structure of the prokaryotic NSS member, LeuT, in a Na + /substrate-bound, inward-facing occluded conformation. To obtain this structure, we were guided by findings from single-molecule fluorescence spectroscopy and molecular dynamics simulations indicating that L-Phe binding and mutation of the conserved N-terminal Trp8 to Ala both promote an inward-facing state. Compared to the outward-facing occluded conformation, our structure reveals a major tilting of the cytoplasmic end of transmembrane segment (TM) 5, which, together with release of the N-terminus but without coupled movement of TM1, opens a wide cavity towards the second Na + binding site. The structure of this key intermediate in the LeuT transport cycle, in the context of other NSS structures, leads to the proposal of an intracellular release mechanism of substrate and ions in NSS proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Molecular Neuropharmacology and Genetics Laboratory, Department of Neuroscience, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, University of Copenhagen, Maersk Tower 7-5, DK-2200, Copenhagen N, Denmark.