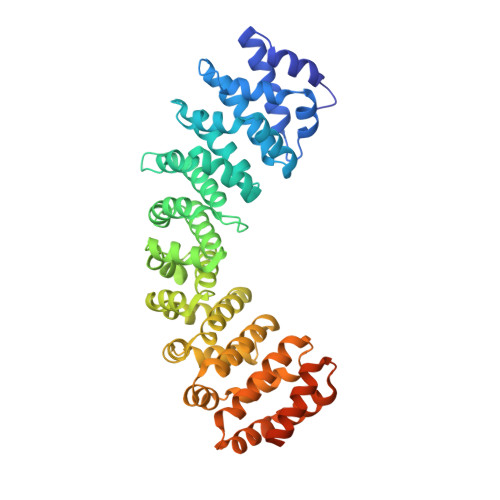
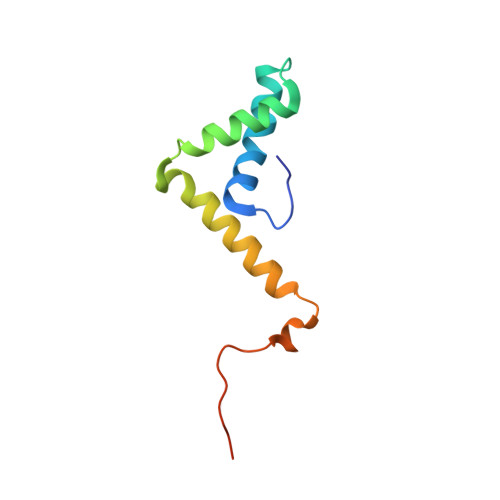
Structural basis for nuclear import selectivity of pioneer transcription factor SOX2.
Jagga, B., Edwards, M., Pagin, M., Wagstaff, K.M., Aragao, D., Roman, N., Nanson, J.D., Raidal, S.R., Dominado, N., Stewart, M., Jans, D.A., Hime, G.R., Nicolis, S.K., Basler, C.F., Forwood, J.K.(2021) Nat Commun 12: 28-28
- PubMed: 33397924
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20194-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6WX7, 6WX8, 6WX9 - PubMed Abstract:
SOX (SRY-related HMG-box) transcription factors perform critical functions in development and cell differentiation. These roles depend on precise nuclear trafficking, with mutations in the nuclear targeting regions causing developmental diseases and a range of cancers. SOX protein nuclear localization is proposed to be mediated by two nuclear localization signals (NLSs) positioned within the extremities of the DNA-binding HMG-box domain and, although mutations within either cause disease, the mechanistic basis has remained unclear. Unexpectedly, we find here that these two distantly positioned NLSs of SOX2 contribute to a contiguous interface spanning 9 of the 10 ARM domains on the nuclear import adapter IMPα3. We identify key binding determinants and show this interface is critical for neural stem cell maintenance and for Drosophila development. Moreover, we identify a structural basis for the preference of SOX2 binding to IMPα3. In addition to defining the structural basis for SOX protein localization, these results provide a platform for understanding how mutations and post-translational modifications within these regions may modulate nuclear localization and result in clinical disease, and also how other proteins containing multiple NLSs may bind IMPα through an extended recognition interface.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Biomedical Sciences, Charles Sturt University, Wagga Wagga, NSW, 2678, Australia.