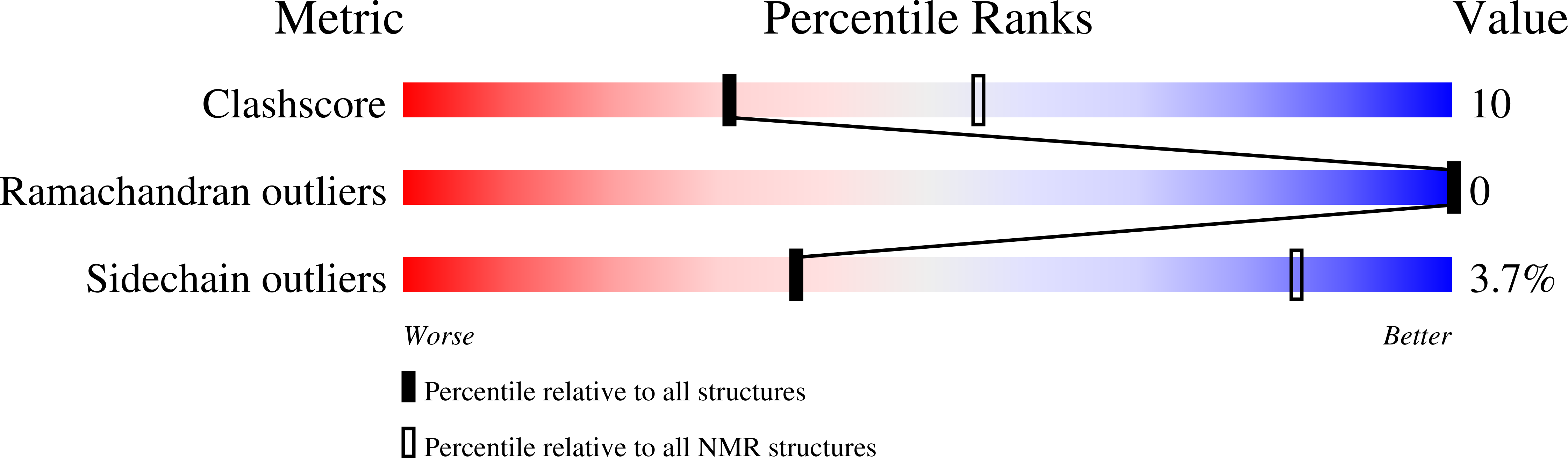
A selective Na V 1.1 activator with potential for treatment of Dravet syndrome epilepsy.
Chow, C.Y., Chin, Y.K.Y., Ma, L., Undheim, E.A.B., Herzig, V., King, G.F.(2020) Biochem Pharmacol 181: 113991-113991
- PubMed: 32335140
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113991
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6V6T - PubMed Abstract:
Dravet syndrome (DS) is a catastrophic epileptic encephalopathy characterised by childhood-onset polymorphic seizures, multiple neuropsychiatric comorbidities, and increased risk of sudden death. Heterozygous loss-of-function mutations in one allele of SCN1A, the gene encoding the voltage-gated sodium channel 1.1 (Na V 1.1), lead to DS. Na V 1.1 is primarily found in the axon initial segment of fast-spiking GABAergic inhibitory interneurons in the brain, and the principle mechanism proposed to underlie seizure genesis in DS is loss of inhibitory input due to dysfunctional firing of GABAergic interneurons. We hypothesised that DS symptoms could be ameliorated by a drug that activates the reduced population of functional Na V 1.1 channels in DS interneurons. We recently identified two homologous disulfide-rich spider-venom peptides (Hm1a and Hm1b) that selectively potentiate Na V 1.1, and showed that selective activation of Na V 1.1 by Hm1a restores the function of inhibitory interneurons in a mouse model of DS. Here we produced recombinant Hm1b (rHm1b) using an E. coli periplasmic expression system, and examined its selectivity against a panel of human Na V subtypes using whole-cell patch-clamp recordings. rHm1b is a potent and highly selective agonist of Na V 1.1 and Na V 1.3 (EC 50 ~12 nM for both). rHm1b is a gating modifier that shifts the voltage dependence of channel activation and inactivation to hyperpolarised and depolarised potentials respectively, presumably by interacting with the channel's voltage-sensor domains. Like Hm1a, the structure of rHm1b determined by using NMR revealed a classical inhibitor cystine knot (ICK) motif. However, we show that rHm1b is an order of magnitude more stable than Hm1a in human cerebrospinal fluid. Overall, our data suggest that rHm1b is an exciting lead for a precision therapeutic targeted against DS.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute for Molecular Bioscience, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, QLD 4072, Australia.