Chemical synthesis and characterization of a new quinazolinedione competitive antagonist for strigolactone receptors with an unexpected binding mode.
Hamiaux, C., Larsen, L., Lee, H.W., Luo, Z., Sharma, P., Hawkins, B.C., Perry, N.B., Snowden, K.C.(2019) Biochem J 476: 1843-1856
- PubMed: 31186286
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20190288
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
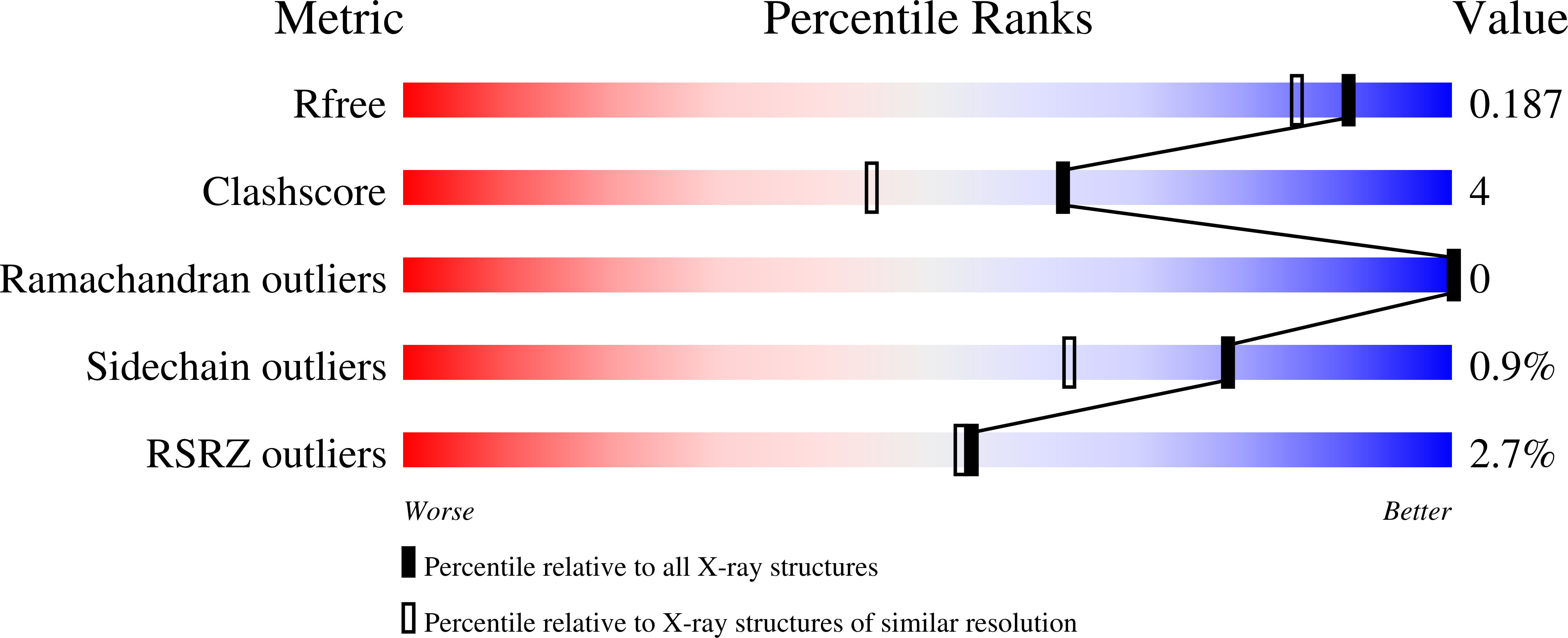
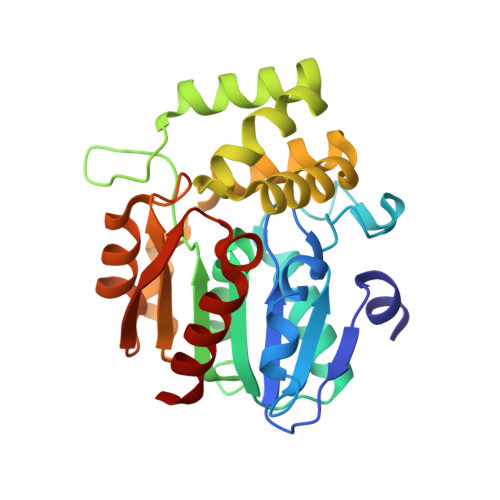
6O5J - PubMed Abstract:
Strigolactones (SLs) are multifunctional plant hormones regulating essential physiological processes affecting growth and development. In vascular plants, SLs are recognized by α/β hydrolase-fold proteins from the D14/DAD2 (Dwarf14/Decreased Apical Dominance 2) family in the initial step of the signaling pathway. We have previously discovered that N -phenylanthranilic acid derivatives (e.g. tolfenamic acid) are potent antagonists of SL receptors, prompting us to design quinazolinone and quinazolinedione derivatives (QADs and QADDs, respectively) as second-generation antagonists. Initial in silico docking studies suggested that these compounds would bind to DAD2, the petunia SL receptor, with higher affinity than the first-generation compounds. However, only one of the QADs/QADDs tested in in vitro assays acted as a competitive antagonist of SL receptors, with reduced affinity and potency compared with its N -phenylanthranilic acid 'parent'. X-ray crystal structure analysis revealed that the binding mode of the active QADD inside DAD2's cavity was not that predicted in silico , highlighting a novel inhibition mechanism for SL receptors. Despite a ∼10-fold difference in potency in vitro , the QADD and tolfenamic acid had comparable activity in planta , suggesting that the QADD compensates for lower potency with increased bioavailability. Altogether, our results establish this QADD as a novel lead compound towards the development of potent and bioavailable antagonists of SL receptors.
Organizational Affiliation:
The New Zealand Institute for Plant and Food Research Limited, Auckland, New Zealand cyril.hamiaux@plantandfood.co.nz.