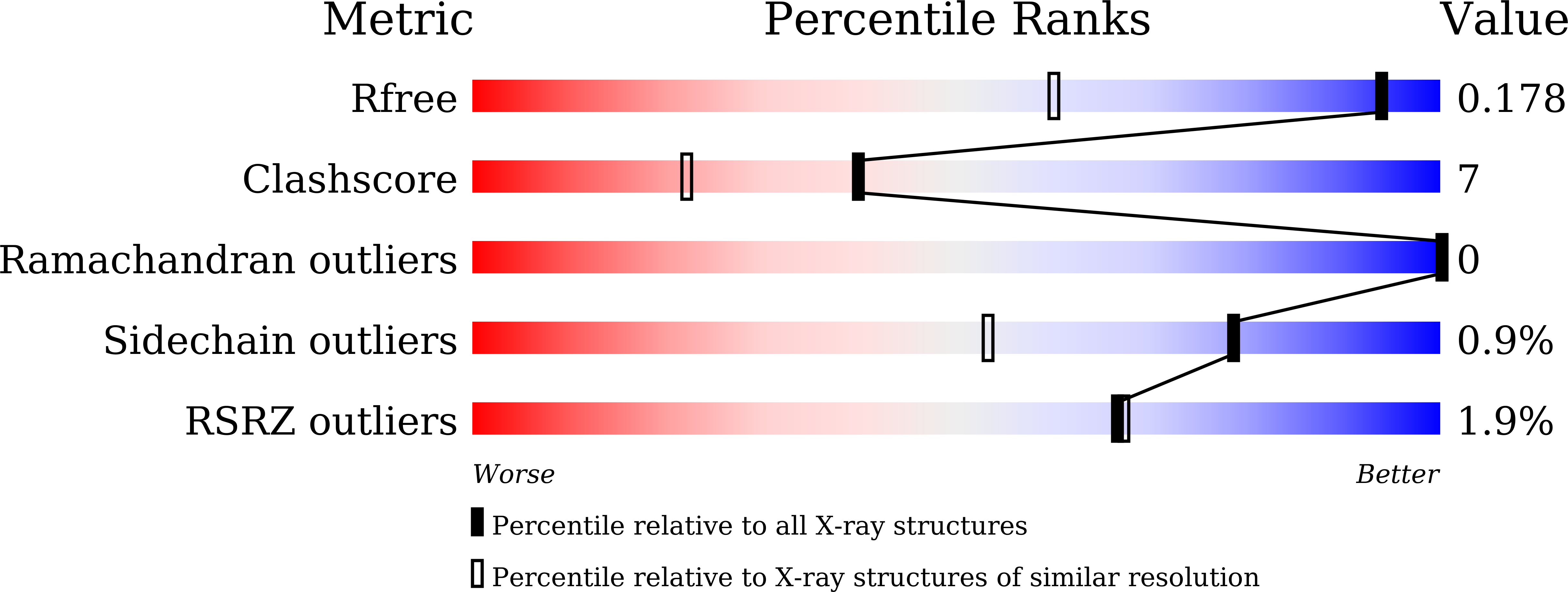
Structural insights into the unique polylactate-degrading mechanism of Thermobifida alba cutinase.
Kitadokoro, K., Kakara, M., Matsui, S., Osokoshi, R., Thumarat, U., Kawai, F., Kamitani, S.(2019) FEBS J 286: 2087-2098
- PubMed: 30761732
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.14781
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6AID - PubMed Abstract:
Cutinases are enzymes known to degrade polyester-type plastics. Est119, a plastic-degrading type of cutinase from Thermobifida alba AHK119 (herein called Ta_cut), shows a broad substrate specificity toward polyesters, and can degrade substrates including polylactic acid (PLA). However, the PLA-degrading mechanism of cutinases is still poorly understood. Here, we report the structure complexes of cutinase with ethyl lactate (EL), the constitutional unit. From this complex structure, the electron density maps clearly showed one lactate (LAC) and one EL occupying different positions in the active site cleft. The binding mode of EL is assumed to show a figure prior to reaction and LAC is an after-reaction product. These complex structures demonstrate the role of active site residues in the esterase reaction and substrate recognition. The complex structures were compared with other documented complex structures of cutinases and with the structure of PETase from Ideonella sakaiensis. The amino acid residues involved in substrate interaction are highly conserved among these enzymes. Thus, mapping the precise interactions in the Ta_cut and EL complex will pave the way for understanding the plastic-degrading mechanism of cutinases and suggest ways of creating more potent enzymes by structural protein engineering.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biomolecular Engineering, Graduate School of Science and Technology, Kyoto Institute of Technology, Japan.