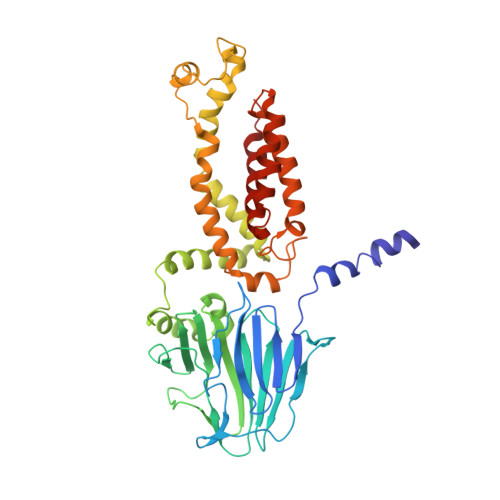
The role of the N-terminal amphipathic helix in bacterial YidC: Insights from functional studies, the crystal structure and molecular dynamics simulations.
Nass, K.J., Ilie, I.M., Saller, M.J., Driessen, A.J.M., Caflisch, A., Kammerer, R.A., Li, X.(2022) Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1864: 183825-183825
- PubMed: 34871574
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2021.183825
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6Y86 - PubMed Abstract:
The evolutionary conserved YidC is a unique dual-function membrane protein that adopts insertase and chaperone conformations. The N-terminal helix of Escherichia coli YidC functions as an uncleaved signal sequence and is important for membrane insertion and interaction with the Sec translocon. Here, we report the first crystal structure of Thermotoga maritima YidC (TmYidC) including the N-terminal amphipathic helix (N-AH) (PDB ID: 6Y86). Molecular dynamics simulations show that N-AH lies on the periplasmic side of the membrane bilayer forming an angle of about 15° with the membrane surface. Our functional studies suggest a role of N-AH for the species-specific interaction with the Sec translocon. The reconstitution data and the superimposition of TmYidC with known YidC structures suggest an active insertase conformation for YidC. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of TmYidC provide evidence that N-AH acts as a membrane recognition helix for the YidC insertase and highlight the flexibility of the C1 region underlining its ability to switch between insertase and chaperone conformations. A structure-based model is proposed to rationalize how YidC performs the insertase and chaperone functions by re-positioning of N-AH and the other structural elements.
Organizational Affiliation:
Photon Science Division, Paul Scherrer Institute, Forschungstrasse 111, 5232 Villigen PSI, Switzerland.