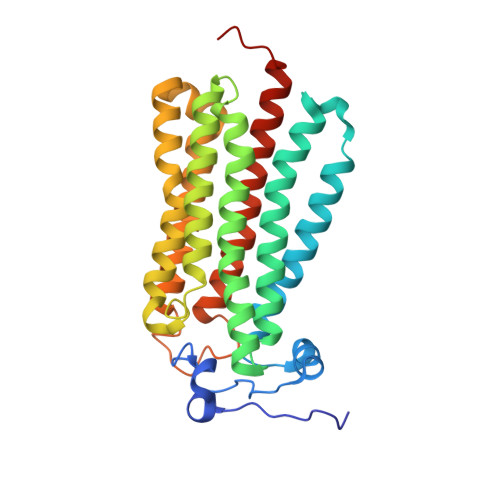
Structural insights into adiponectin receptors suggest ceramidase activity.
Vasiliauskaite-Brooks, I., Sounier, R., Rochaix, P., Bellot, G., Fortier, M., Hoh, F., De Colibus, L., Bechara, C., Saied, E.M., Arenz, C., Leyrat, C., Granier, S.(2017) Nature 6: 120-123
- PubMed: 28329765
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21714
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5LWY, 5LX9, 5LXA, 5LXG - PubMed Abstract:
Adiponectin receptors (ADIPORs) are integral membrane proteins that control glucose and lipid metabolism by mediating, at least in part, a cellular ceramidase activity that catalyses the hydrolysis of ceramide to produce sphingosine and a free fatty acid (FFA). The crystal structures of the two receptor subtypes, ADIPOR1 and ADIPOR2, show a similar overall seven-transmembrane-domain architecture with large unoccupied cavities and a zinc binding site within the seven transmembrane domain. However, the molecular mechanisms by which ADIPORs function are not known. Here we describe the crystal structure of ADIPOR2 bound to a FFA molecule and show that ADIPOR2 possesses intrinsic basal ceramidase activity that is enhanced by adiponectin. We also identify a ceramide binding pose and propose a possible mechanism for the hydrolytic activity of ADIPOR2 using computational approaches. In molecular dynamics simulations, the side chains of residues coordinating the zinc rearrange quickly to promote the nucleophilic attack of a zinc-bound hydroxide ion onto the ceramide amide carbonyl. Furthermore, we present a revised ADIPOR1 crystal structure exhibiting a seven-transmembrane-domain architecture that is clearly distinct from that of ADIPOR2. In this structure, no FFA is observed and the ceramide binding pocket and putative zinc catalytic site are exposed to the inner membrane leaflet. ADIPOR1 also possesses intrinsic ceramidase activity, so we suspect that the two distinct structures may represent key steps in the enzymatic activity of ADIPORs. The ceramidase activity is low, however, and further studies will be required to characterize fully the enzymatic parameters and substrate specificity of ADIPORs. These insights into ADIPOR function will enable the structure-based design of potent modulators of these clinically relevant enzymes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institut de Génomique Fonctionnelle, CNRS UMR-5203 INSERM U1191, University of Montpellier, 34094 Montpellier, France.