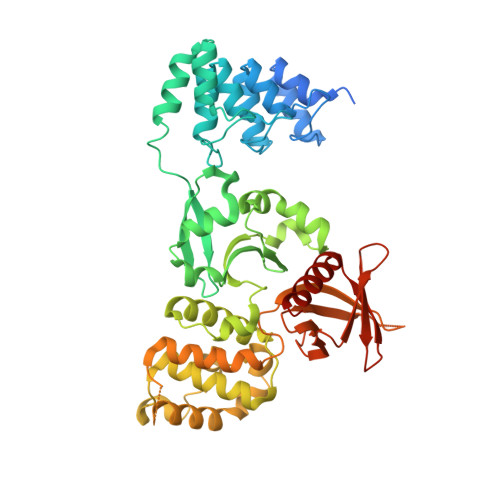
Structural analysis of the KRIT1 ankyrin repeat and FERM domains reveals a conformationally stable ARD-FERM interface.
Zhang, R., Li, X., Boggon, T.J.(2015) J Struct Biol 192: 449-456
- PubMed: 26458359
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2015.10.006
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5D68 - PubMed Abstract:
Cerebral cavernous malformations (CCM) are vascular dysplasias that usually occur in the brain and are associated with mutations in the KRIT1/CCM1, CCM2/MGC4607/OSM/Malcavernin, and PDCD10/CCM3/TFAR15 genes. Here we report the 2.9 Å crystal structure of the ankyrin repeat domain (ARD) and FERM domain of the protein product of KRIT1 (KRIT1; Krev interaction trapped 1). The crystal structure reveals that the KRIT1 ARD contains 4 ankyrin repeats. There is an unusual conformation in the ANK4 repeat that is stabilized by Trp-404, and the structure reveals a solvent exposed ankyrin groove. Domain orientations of the three copies within the asymmetric unit suggest a stable interaction between KRIT1 ARD and FERM domains, indicating a globular ARD-FERM module. This resembles the additional F0 domain found N-terminal to the FERM domain of talin. Structural analysis of KRIT1 ARD-FERM highlights surface regions of high evolutionary conservation, and suggests potential sites that could mediate interaction with binding partners. The structure therefore provides a better understanding of KRIT1 at the molecular level.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Pharmacology, Yale University School of Medicine, 333 Cedar Street, New Haven, CT 06520, USA.