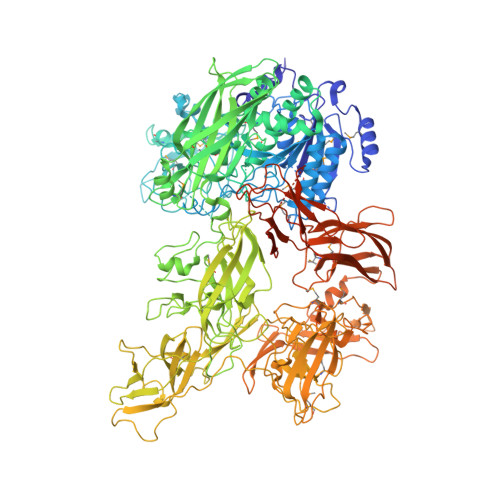
Structure of ScpC, a virulence protease fromStreptococcus pyogenes, reveals the functional domains and maturation mechanism.
Jobichen, C., Tan, Y.C., Prabhakar, M.T., Nayak, D., Biswas, D., Pannu, N.S., Hanski, E., Sivaraman, J.(2018) Biochem J 475: 2847-2860
- PubMed: 30049896
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20180145
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5XXZ, 5XYA, 5XYR - PubMed Abstract:
Group A Streptococcus (GAS; Streptococcus pyogenes ) causes a wide range of infections, including pharyngitis, impetigo, and necrotizing fasciitis, and results in over half a million deaths annually. GAS ScpC (SpyCEP), a 180-kDa surface-exposed, subtilisin-like serine protease, acts as an essential virulence factor that helps S. pyogenes evade the innate immune response by cleaving and inactivating C-X-C chemokines. ScpC is thus a key candidate for the development of a vaccine against GAS and other pathogenic streptococcal species. Here, we report the crystal structures of full-length ScpC wild-type, the inactive mutant, and the ScpC-AEBSF inhibitor complex. We show ScpC to be a multi-domain, modular protein consisting of nine structural domains, of which the first five constitute the PR + A region required for catalytic activity. The four unique C-terminal domains of this protein are similar to collagen-binding and pilin proteins, suggesting an additional role for ScpC as an adhesin that might mediate the attachment of S. pyogenes to various host tissues. The Cat domain of ScpC is similar to subtilisin-like proteases with significant difference to dictate its specificity toward C-X-C chemokines. We further show that ScpC does not undergo structural rearrangement upon maturation. In the ScpC-inhibitor complex, the bound inhibitor breaks the hydrogen bond between active-site residues, which is essential for catalysis. Guided by our structure, we designed various epitopes and raised antibodies capable of neutralizing ScpC activity. Collectively, our results demonstrate the structure, maturation process, inhibition, and substrate recognition of GAS ScpC, and reveal the presence of functional domains at the C-terminal region.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, 14 Science Drive 4, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117543.