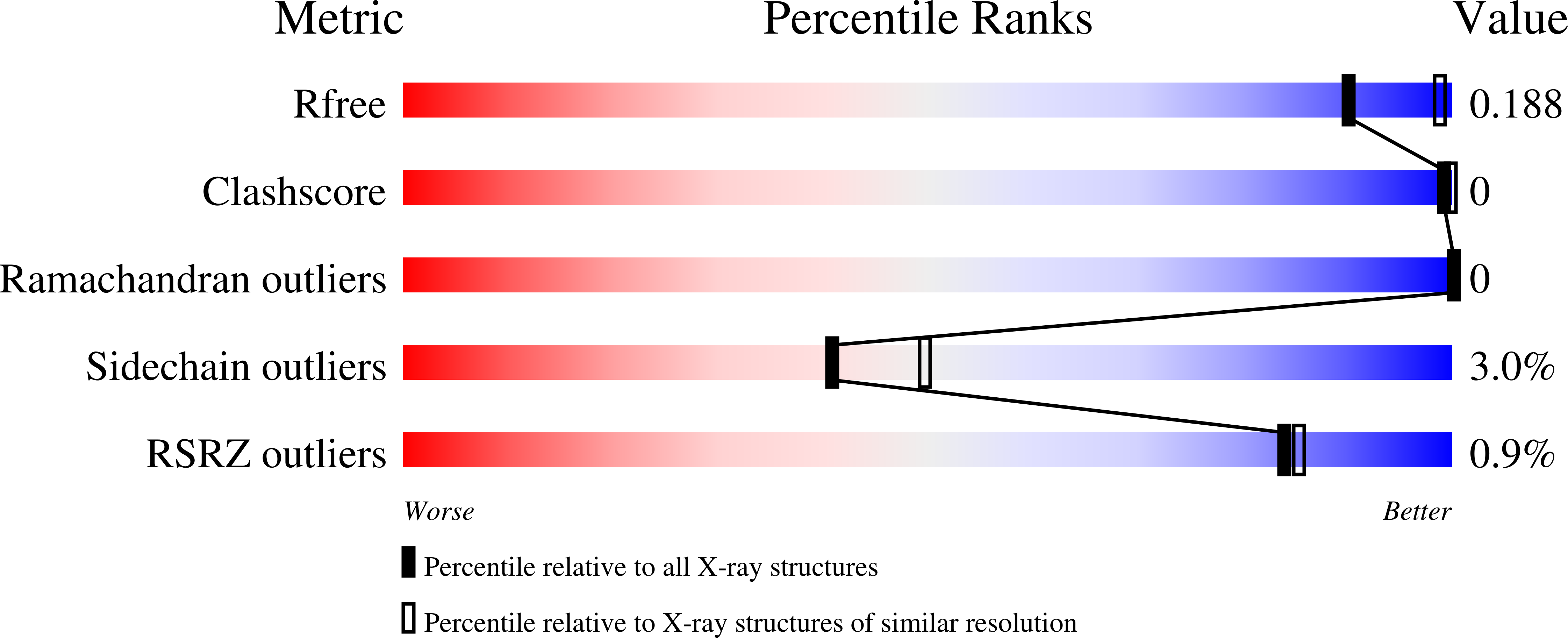
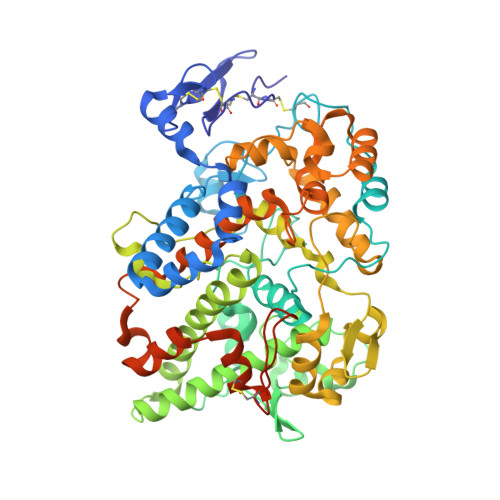
Dual cyclooxygenase-fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor exploits novel binding interactions in the cyclooxygenase active site.
Goodman, M.C., Xu, S., Rouzer, C.A., Banerjee, S., Ghebreselasie, K., Migliore, M., Piomelli, D., Marnett, L.J.(2018) J Biol Chem 293: 3028-3038
- PubMed: 29326169
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.802058
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5W58 - PubMed Abstract:
The cyclooxygenases COX-1 and COX-2 oxygenate arachidonic acid (AA) to prostaglandin H 2 (PGH 2 ). COX-2 also oxygenates the endocannabinoids 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) and arachidonoylethanolamide (AEA) to the corresponding PGH 2 analogs. Both enzymes are targets of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), but NSAID-mediated COX inhibition is associated with gastrointestinal toxicity. One potential strategy to counter this toxicity is to also inhibit fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), which hydrolyzes bioactive fatty acid ethanolamides (FAEs) into fatty acids and ethanolamine. Here, we investigated the mechanism of COX inhibition by ARN2508, an NSAID that inhibits both COXs and FAAH with high potency, target selectivity, and decreased gastrointestinal toxicity in mouse models, presumably due to its ability to increase levels of FAEs. A 2.27-Å-resolution X-ray crystal structure of the COX-2·( S )-ARN2508 complex reveals that ARN2508 adopts a binding pose similar to that of its parent NSAID flurbiprofen. However, ARN2508's alkyl tail is inserted deep into the top channel, an active site region not exploited by any previously reported NSAID. As for flurbiprofen, ARN2508's potency is highly dependent on the configuration of the α-methyl group. Thus, ( S )-ARN2508 is more potent than ( R )-ARN2508 for inhibition of AA oxygenation by both COXs and 2-AG oxygenation by COX-2. Also, similarly to ( R )-flurbiprofen, ( R )-ARN2508 exhibits substrate selectivity for inhibition of 2-AG oxygenation. Site-directed mutagenesis confirms the importance of insertion of the alkyl tail into the top channel for ( S )-ARN2508's potency and suggests a role for Ser-530 as a determinant of the inhibitor's slow rate of inhibition compared with that of ( S )-flurbiprofen.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the A. B. Hancock, Jr. Memorial Laboratory for Cancer Research, Departments of Biochemistry, Chemistry, and Pharmacology, Vanderbilt Institute of Chemical Biology and Center in Molecular Toxicology, Vanderbilt Ingram Cancer Center, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, Tennessee 37232.