A stereospecific carboxyl esterase from Bacillus coagulans hosting nonlipase activity within a lipase-like fold.
De Vitis, V., Nakhnoukh, C., Pinto, A., Contente, M.L., Barbiroli, A., Milani, M., Bolognesi, M., Molinari, F., Gourlay, L.J., Romano, D.(2018) FEBS J 285: 903-914
- PubMed: 29278448
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.14368
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5O7G, 5OLU - PubMed Abstract:
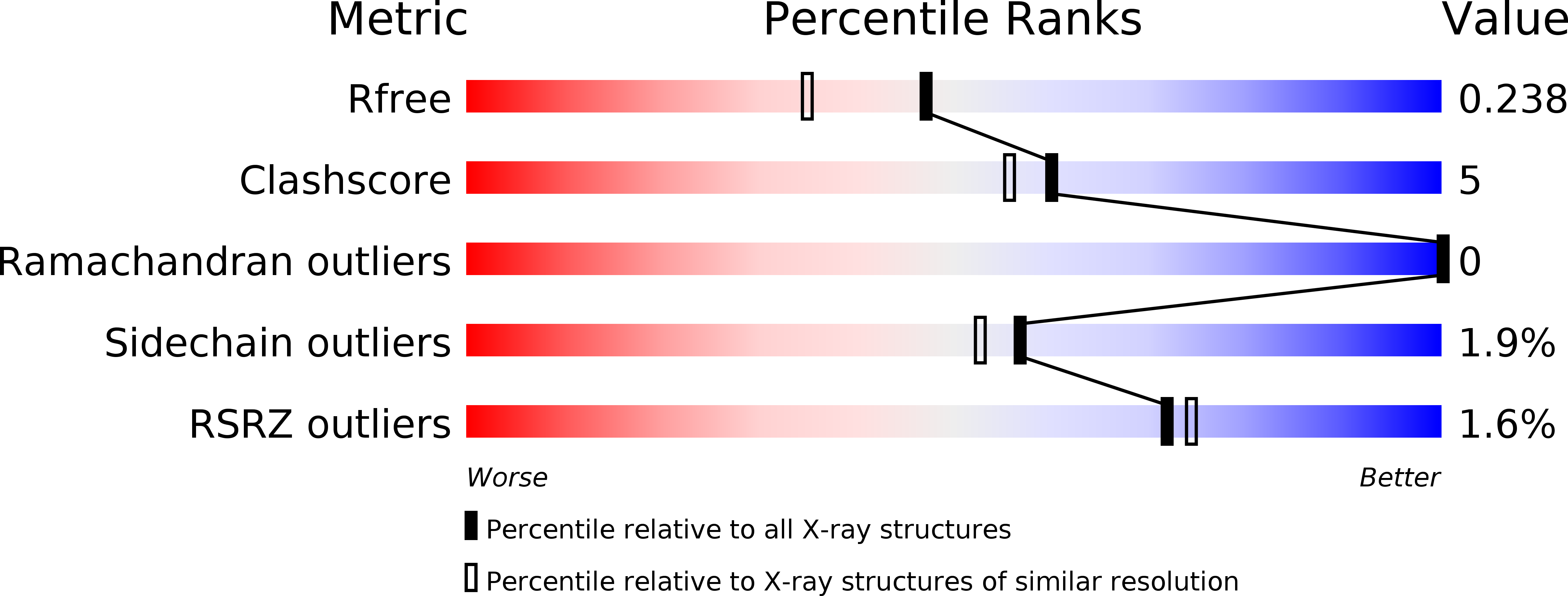
Microbial carboxylesterases are important biocatalysts that selectively hydrolyze an extensive range of esters. Here, we report the biochemical and structural characterization of an atypical carboxylesterase from Bacillus coagulans (BCE), endowed with high enantioselectivity toward different 1,2-O-isopropylideneglycerol (IPG or solketal) esters. BCE efficiently catalyzes the production of enantiopure (S)-IPG, a chiral building block for the synthesis of β-blockers, glycerophospholipids, and prostaglandins; efficient hydrolysis was observed up to 65 °C. To gain insight into the mechanistic bases of such enantioselectivity, we solved the crystal structures of BCE in apo- and glycerol-bound forms at resolutions of 1.9 and 1.8 Å, respectively. In silico docking studies on the BCE structure confirmed that IPG esters with small acyl chains (≤ C6) were easily accommodated in the active site pocket, indicating that small conformational changes are necessary to accept longer substrates. Furthermore, docking studies suggested that enantioselectivity may be due to an improved stabilization of the tetrahedral reaction intermediate for the S-enantiomer. Contrary to the above functional data implying nonlipolytic functions, BCE displays a lipase-like 3D structure that hosts a "lid" domain capping the main entrance to the active site. In lipases the lid mediates catalysis through interfacial activation, a process that we did not observe for BCE. Overall, we present the functional-structural properties of an atypical carboxyl esterase that has nonlipase-like functions, yet possesses a lipase-like 3D fold. Our data provide original enzymatic information in view of BCE applications as an inexpensive, efficient biocatalyst for the production of enantiopure (S)-IPG. Coordinates and structure factors have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank (www.rcsb.org) under accession numbers 5O7G (apo-BCE) and 5OLU (glycerol-bound BCE).
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Food, Environmental and Nutritional Sciences (DeFENS), Università degli Studi di Milano, Italy.