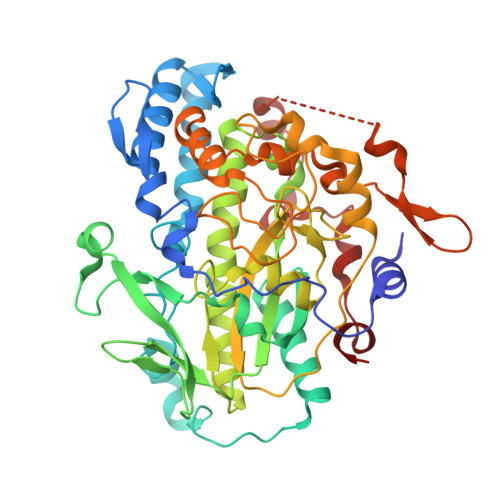
Cobamide-mediated enzymatic reductive dehalogenation via long-range electron transfer.
Kunze, C., Bommer, M., Hagen, W.R., Uksa, M., Dobbek, H., Schubert, T., Diekert, G.(2017) Nat Commun 8: 15858-15858
- PubMed: 28671181
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15858
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
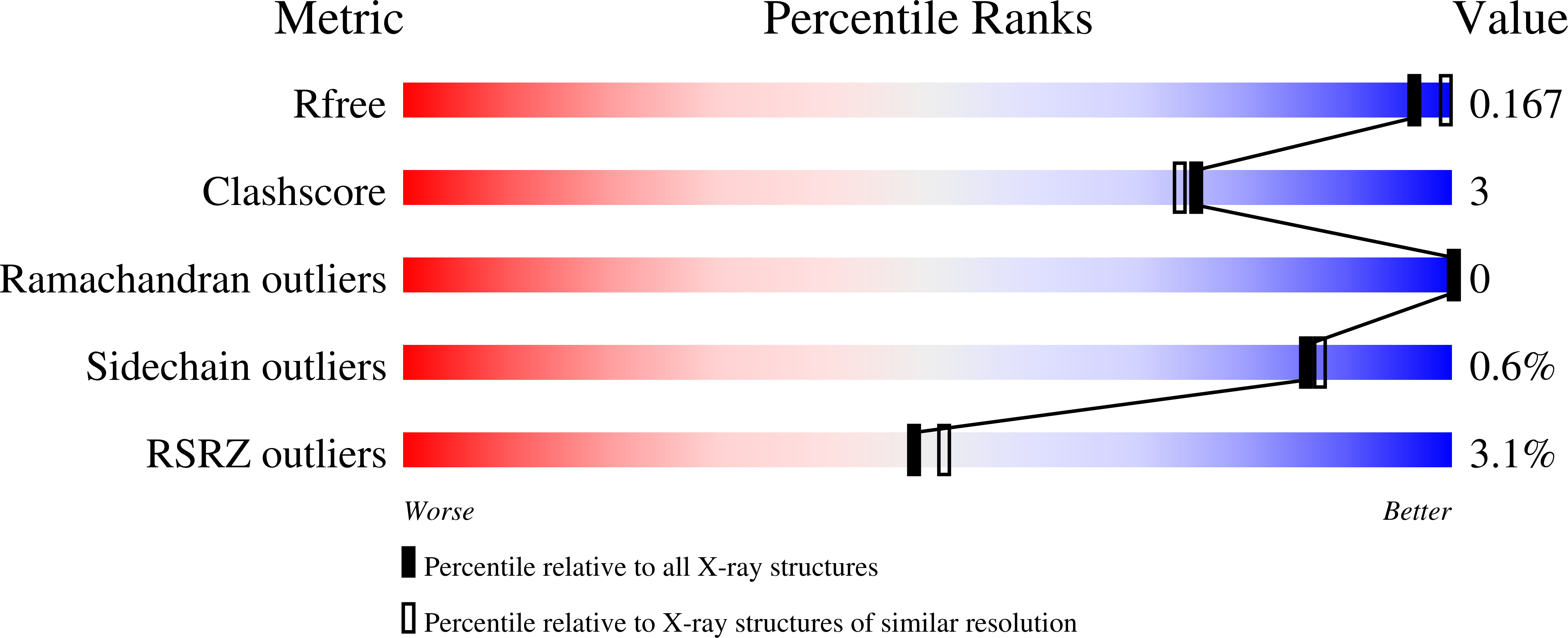
5M2G, 5M8U, 5M8W, 5M8X, 5M8Y, 5M8Z, 5M90, 5M91, 5M92, 5MA0, 5MA1, 5MA2, 5MAA - PubMed Abstract:
The capacity of metal-containing porphyrinoids to mediate reductive dehalogenation is implemented in cobamide-containing reductive dehalogenases (RDases), which serve as terminal reductases in organohalide-respiring microbes. RDases allow for the exploitation of halogenated compounds as electron acceptors. Their reaction mechanism is under debate. Here we report on substrate-enzyme interactions in a tetrachloroethene RDase (PceA) that also converts aryl halides. The shape of PceA's highly apolar active site directs binding of bromophenols at some distance from the cobalt and with the hydroxyl substituent towards the metal. A close cobalt-substrate interaction is not observed by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. Nonetheless, a halogen substituent para to the hydroxyl group is reductively eliminated and the path of the leaving halide is traced in the structure. Based on these findings, an enzymatic mechanism relying on a long-range electron transfer is concluded, which is without parallel in vitamin B 12 -dependent biochemistry and represents an effective mode of RDase catalysis.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Applied and Ecological Microbiology, Institute of Microbiology, Friedrich Schiller University, Philosophenweg 12, Jena D-07743, Germany.