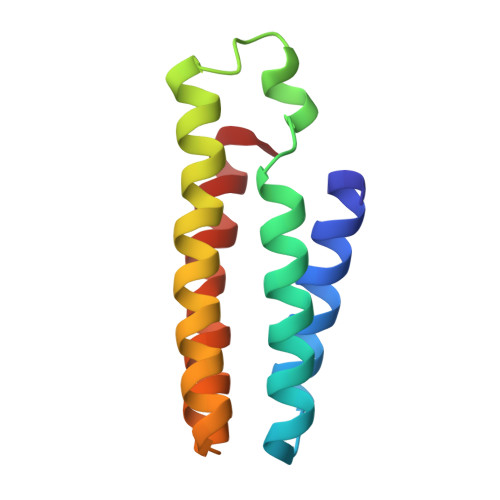
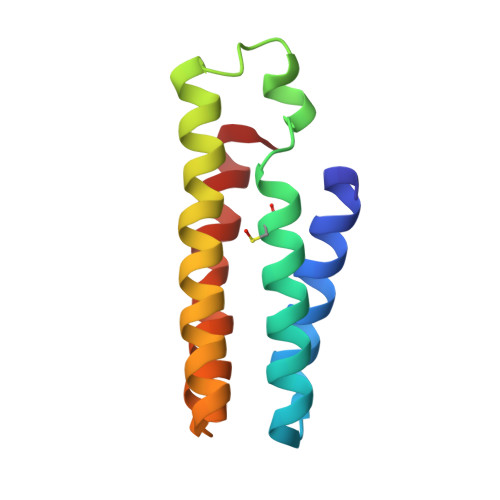
De Novo Design of an Allosteric Metalloprotein Assembly with Strained Disulfide Bonds.
Churchfield, L.A., Medina-Morales, A., Brodin, J.D., Perez, A., Tezcan, F.A.(2016) J Am Chem Soc 138: 13163-13166
- PubMed: 27649076
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.6b08458
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5L31, 5L32 - PubMed Abstract:
A major goal in metalloprotein design is to build protein scaffolds from scratch that allow precise control over metal coordination. A particular challenge in this regard is the construction of allosteric systems in which metal coordination equilibria are coupled to other chemical events that take place elsewhere in the protein scaffold. We previously developed a metal-templated self-assembly strategy (MeTIR) to build supramolecular protein complexes with tailorable interfaces from monomeric building blocks. Here, using this strategy, we have incorporated multiple disulfide bonds into the interfaces of a Zn-templated cytochrome cb 562 assembly in order to create mechanical strain on the quaternary structural level. Structural and biophysical analyses indicate that this strain leads to an allosteric system in which Zn 2+ binding and dissociation are remotely coupled to the formation and breakage of a disulfide bond over a distance of >14 Å. The breakage of this strained bond upon Zn 2+ dissociation occurs in the absence of any reductants, apparently through a hydrolytic mechanism that generates a sulfenic acid/thiol pair.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of California, San Diego , La Jolla, California 92093-0356, United States.