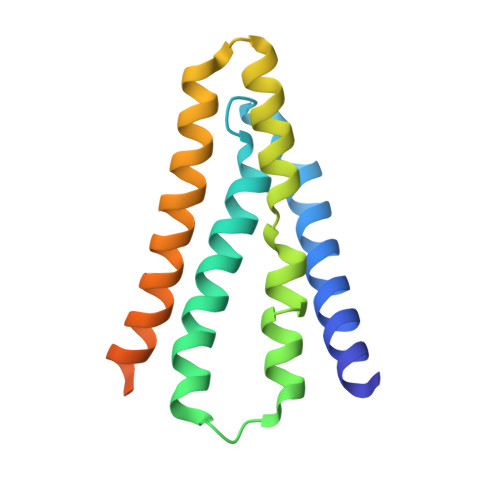
Mechanistic signs of double-barreled structure in a fluoride ion channel.
Last, N.B., Kolmakova-Partensky, L., Shane, T., Miller, C.(2016) Elife 5
- PubMed: 27449280
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18767
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5KBN, 5KOM - PubMed Abstract:
The Fluc family of F(-) ion channels protects prokaryotes and lower eukaryotes from the toxicity of environmental F(-). In bacteria, these channels are built as dual-topology dimers whereby the two subunits assemble in antiparallel transmembrane orientation. Recent crystal structures suggested that Fluc channels contain two separate ion-conduction pathways, each with two F(-) binding sites, but no functional correlates of this unusual architecture have been reported. Experiments here fill this gap by examining the consequences of mutating two conserved F(-)-coordinating phenylalanine residues. Substitution of each phenylalanine specifically extinguishes its associated F(-) binding site in crystal structures and concomitantly inhibits F(-) permeation. Functional analysis of concatemeric channels, which permit mutagenic manipulation of individual pores, show that each pore can be separately inactivated without blocking F(-) conduction through its symmetry-related twin. The results strongly support dual-pathway architecture of Fluc channels.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Brandeis University, Waltham, United States.